Page 97 - A Handbook for Academia, Industry and Policymakers: Reinforcing the Innovation-Employability Nexus in the Mediterranean
P. 97
96 REINFORCING THE INNOVATION-EMPLOYABILITY NEXUS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN REINFORCING THE INNOVATION-EMPLOYABILITY NEXUS IN THE MEDITERRANEAN 97
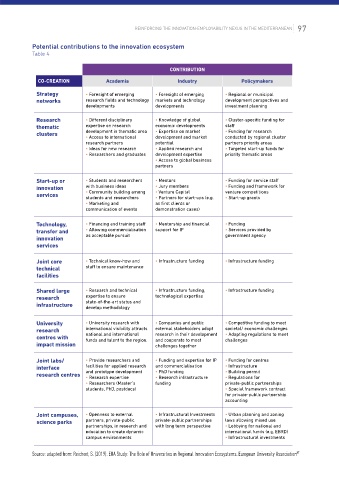
POLICYMAKERS INTERMEDIARY ORGANISATIONS Potential contributions to the innovation ecosystem
Table 4
For the development of effective knowledge Intermediaries play a pivotal role in knowledge
exchange innovation systems, public authorities, and innovation ecosystems. They act as agents CONTRIBUTION
and governments – national, regional, and local – or brokers in aspects of the innovation process
need to create innovation-conducive framework between two or more parties. Intermediaries CO-CREATION Academia Industry Policymakers
conditions, acting as primary regulator and funder, can be cooperative technical organisations (e.g.
infrastructural developer as well as strategy industry associations) , business incubators, Strategy • Foresight of emerging • Foresight of emerging • Regional or municipal
89
research fields and technology
development perspectives and
markets and technology
networks
moderator and facilitator. In the Mediterranean innovation platforms, NGOs and consultancies developments developments investment planning
region, the European Bank for Reconstruction or innovation market-place operators. Since
and Development (EBRD) is active in liaising with the early 2000s, intermediaries strengthened Research • Different disciplinary • Knowledge of global • Cluster-specific funding for
policymakers and industry to support the needs the capacity and coordination of innovation thematic expertise on research economic developments staff
• Funding for research
• Expertise on market
development in thematic area
of small and medium sized companies. They have processes90. These ‘systemic’ intermediaries act clusters • Access to international development and market conducted by regional cluster
provided advocacy in Egypt in the manufacturing as boundary spanners and facilitate cooperation research partners potential partners priority areas
and tourism sectors to help express the needs between different actors. They can close cognitive, • Ideas for new research • Applied research and • Targeted start-up funds for
development expertise
• Researchers and graduates
priority thematic areas
for stronger governance to improve quality normative, and managerial gaps that can present • Access to global business
through qualification and occupational skill barriers to a well-functioning innovation system. partners
standards as well as curricula at the national Intermediary activities include 91,92 :
level. Details about EBRD can be found at the end Start-up or • Students and researchers • Mentors • Funding for service staff
• Jury members
• Funding and framework for
with business ideas
of this chapter. See Table 4 for a list of potential Awareness and exchange of knowledge innovation • Community building among • Venture Capital venture competitions
contributions from stakeholders. services students and researchers • Partners for start-ups (e.g. • Start-up grants
Advisory, consultancy and backstopping (e.g. • Marketing and as first clients or
providing information about potential communication of events demonstration cases)
INDUSTRY
collaborators)
Organisations (companies, public institutions Technology, • Financing and training staff • Mentorship and financial • Funding
and the third sector ) often cannot depend Demand articulation transfer and • Allowing commercialisation support for IP • Services provided by
as acceptable pursuit
government agency
exclusively on their internal research and Facilitation and brokerage across networks, innovation
development process to match the increased (e.g. acting as a mediator in between services
pace of innovation. This is especially true for organisations)
small and medium-sized companies. As a result, Joint core • Technical know-how and • Infrastructure funding • Infrastructure funding
staff to ensure maintenance
technical
HEIs have become important partners, providing Capacity building facilities
the most needed resource – competent graduates
– while continuously generating new knowledge, Supporting access to resources Shared large • Research and technical • Infrastructure funding, • Infrastructure funding
including research-based solutions to specific research expertise to ensure technological expertise
innovation challenges. Just as vitally, universities Validation and regulation infrastructure state-of-the-art status and
are naturally disposed to scan knowledge Protecting results develop methodology
frontiers and explore the next generation of
technologies. They can thus identify new kinds Commercialisation University • University research with • Companies and public • Competitive funding to meet
international visibility attracts
societal/ economic challenges
external stakeholders adopt
research
of technological, environmental, and societal centres with national and international research in their development • Adapting regulations to meet
challenges which define future market trends. Evaluation of outcomes impact mission funds and talent to the region. and cooperate to meet challenges
challenges together
They look for new and often interdisciplinary
approaches for addressing such challenges, Joint labs/ • Provide researchers and • Funding and expertise for IP • Funding for centres
expanding their horizons, and developing new interface facilities for applied research and commercialisation • Infrastructure
pathways. In order to fully benefit from such research centres and prototype development • PhD funding • Building permit
dense collaborative networks of open innovation, • Research expertise • Research infrastructure • Regulations for
• Researchers (Master’s
funding
private-public partnerships
industry needs some enabling conditions, such students, PhD, postdocs) • Special framework contract
as skilled experts, relevant research centres for private-public partnership
and innovation platforms that bring together accounting
relevant actors. See Table 4 for a list of potential Joint campuses, • Openness to external • Infrastructural Investments • Urban planning and zoning
contributions. science parks partners, private-public private-public partnerships laws allowing mixed use
partnerships, in research and with long term perspective • Lobbying for national and
education to create dynamic international funds (e.g. EBRD)
campus environments • Infrastructural investments
Source: adapted from: Reichert, S. (2019). EUA Study: The Role of Universities in Regional Innovation Ecosystems. European University Association 87