Page 43 - NUMINO TG_3A
P. 43
012_G3U2_TG_CA 2011.4.6 12:30 PM ˘ ` 026 PDF_In 2540DPI 150LPI T
Activity 3 Skip-Counting
jOb ective Skip-count to understand the order of 4-digit numbers.
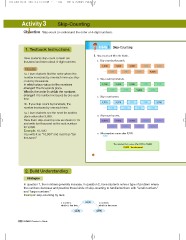
1. Textbook Instructions Activity 3 Skip-Counting
Have students skip-count to learn ten 1 . Skip-count and fill in the blanks.
thousand and learn about 4-digit numbers.
a. Skip-count by thousands.
1a. Have students find the order where the
number increases by one each time you skip- 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000
count by thousands.
In which place value do the numbers 6,000 7,000 8,000 9,000
change? The thousands place.
What is the order in which the numbers b. Skip-count by hundreds.
change? The number increases by one each
time. 9,100 9,200 9,300 9,400 9,500
1b. If you skip-count by hundreds, the 9,600 9,700 9,800 9,900
number increases by one each time.
c. Skip-count by tens.
1e. Have students see the need for another
place value after 9,999. 9,910 9,920 9,930 9,940 9,950
Have them skip-count by one as shown in 1d.
and write ten thousand as the next number 9,960 9,970 9,980 9,990
for 9,999.
Example: 10, 000 d. Skip-count by ones.
You write it as “10,000” and read it as “ten
thousand.” 9,991 9,992 9,993 9,994 9,995
9,996 9,997 9,998 9,999
e. What number comes after 9,999?
10,000
The number that comes after 9,999 is 10,000.
10,000 Ten thousand
18
2. Build Understanding
In question 1, the numbers generally increase. In question 2, have students solve a type of problem where
the numbers decrease and practice these kinds of skip-counting to familiarize them with “small numbers”
and “large numbers.”
Example: skip-counting by tens
a number, 4240 a number,
which is ten less which is ten more
4230 4250
026 NUMINO Teacher s Guide
Activity 3 Skip-Counting
jOb ective Skip-count to understand the order of 4-digit numbers.
1. Textbook Instructions Activity 3 Skip-Counting
Have students skip-count to learn ten 1 . Skip-count and fill in the blanks.
thousand and learn about 4-digit numbers.
a. Skip-count by thousands.
1a. Have students find the order where the
number increases by one each time you skip- 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000
count by thousands.
In which place value do the numbers 6,000 7,000 8,000 9,000
change? The thousands place.
What is the order in which the numbers b. Skip-count by hundreds.
change? The number increases by one each
time. 9,100 9,200 9,300 9,400 9,500
1b. If you skip-count by hundreds, the 9,600 9,700 9,800 9,900
number increases by one each time.
c. Skip-count by tens.
1e. Have students see the need for another
place value after 9,999. 9,910 9,920 9,930 9,940 9,950
Have them skip-count by one as shown in 1d.
and write ten thousand as the next number 9,960 9,970 9,980 9,990
for 9,999.
Example: 10, 000 d. Skip-count by ones.
You write it as “10,000” and read it as “ten
thousand.” 9,991 9,992 9,993 9,994 9,995
9,996 9,997 9,998 9,999
e. What number comes after 9,999?
10,000
The number that comes after 9,999 is 10,000.
10,000 Ten thousand
18
2. Build Understanding
In question 1, the numbers generally increase. In question 2, have students solve a type of problem where
the numbers decrease and practice these kinds of skip-counting to familiarize them with “small numbers”
and “large numbers.”
Example: skip-counting by tens
a number, 4240 a number,
which is ten less which is ten more
4230 4250
026 NUMINO Teacher s Guide