Page 116 - The Miracle in the Cell
P. 116
THE MIRACLE IN THE CELL
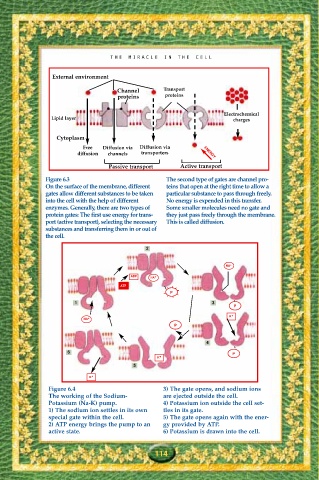
External environment
Channel Transport
proteins proteins
Electrochemical
Lipid layer charges
Cytoplasm
Free Diffusion via Diffusion via
diffusion channels transporters ENERGY
Passive transport Active transport
Figure 6.3 The second type of gates are channel pro-
On the surface of the membrane, different teins that open at the right time to allow a
gates allow different substances to be taken particular substance to pass through freely.
into the cell with the help of different No energy is expended in this transfer.
enzymes. Generally, there are two types of Some smaller molecules need no gate and
protein gates: The first use energy for trans- they just pass freely through the membrane.
port (active transport), selecting the necessary This is called diffusion.
substances and transferring them in or out of
the cell.
2
NA +
ADP NA +
ATP
P
1 3
P
K +
NA +
P
4
6 P
K +
5
K +
Figure 6.4 3) The gate opens, and sodium ions
The working of the Sodium- are ejected outside the cell.
Potassium (Na-K) pump. 4) Potassium ion outside the cell set-
1) The sodium ion settles in its own tles in its gate.
special gate within the cell. 5) The gate opens again with the ener-
2) ATP energy brings the pump to an gy provided by ATP.
active state. 6) Potassium is drawn into the cell.
114