Page 109 - The Miracle of the Blood and Heart
P. 109
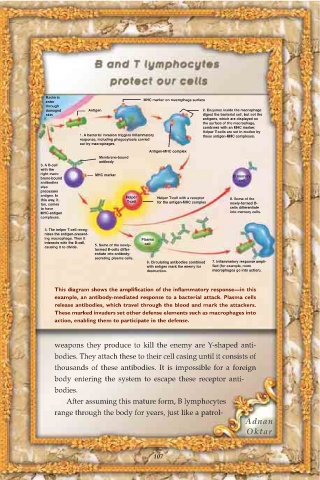
Bacteria
enter MHC marker on macrophage surface
through
damaged Antigen 2. Enzymes inside the macrophage
skin digest the bacterial cell, but not the
antigens, which are displayed on
the surface of the macrophage,
combined with an MHC marker.
Helper T-cells are set in motion by
1. A bacterial invasion triggers inflammatory these antigen-MHC complexes.
response, including phagocytosis carried
out by macrophages.
Antigen-MHC complex
Membrane-bound
antibody
3. A B-cell
with the
right mem- MHC marker B memory
brane-bound cell
antibodies
also
processes
antigen. In Helper Helper T-cell with a receptor
this way, it, T-cell for the antigen-MHC complex 8. Some of the
too, comes newly-formed B-
to have cells differentiate
MHC-antigen into memory cells.
complexes.
4. The helper T-cell recog-
nizes the antigen-present-
ing macrophage. Then it Plasma
interacts with the B-cell, 5. Some of the newly- cell
causing it to divide.
formed B-cells differ-
entiate into antibody-
secreting plasma cells.
6. Circulating antibodies combined 7. Inflammatory response ampli-
with antigen mark the enemy for fied (for example, more
destruction. macrophages go into action).
This diagram shows the amplification of the inflammatory response—in this
example, an antibody-mediated response to a bacterial attack. Plasma cells
release antibodies, which travel through the blood and mark the attackers.
These marked invaders set other defense elements such as macrophages into
action, enabling them to participate in the defense.
weapons they produce to kill the enemy are Y-shaped anti-
bodies. They attach these to their cell casing until it consists of
thousands of these antibodies. It is impossible for a foreign
body entering the system to escape these receptor anti-
bodies.
After assuming this mature form, B lymphocytes
range through the body for years, just like a patrol-
Adnan
Oktar
107