Page 3 - Mechanics of Structures – Chapter 1
P. 3
Mechanics of Civil Engineering Structures – Chapter 5
7.2.1 Single Shear
"Single shear" refers to the fact that there is a single plane of shear force through the fastener -
an example would be a tie rod end stud. Even with the taper to locate the parts, there is a single
shear plane - it exists between the tie rod end housing and the knuckle surface (typically
considered to be even with the lower plane of the knuckle surface.)
,
, = n = no. of planes = 1
7.2.2 Double Shear
"Double shear" would mean that there are two shear planes through the fastener, or that the
total shear force is "split" into two locations on the fastener body. It's most common to see hitch
pins loaded in double shear - a good example of this would be the cross pin for your trailer hitch.
,
, = , n = ≥ 2
,
, = , [Rectangular cross section]
2
,
, = , [circular cross section]
2 2/4
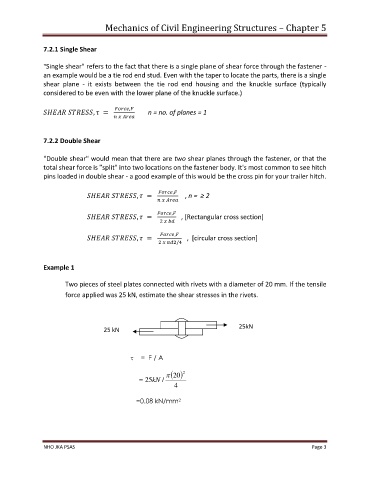
Example 1
Two pieces of steel plates connected with rivets with a diameter of 20 mm. If the tensile
force applied was 25 kN, estimate the shear stresses in the rivets.
25kN
30k
25 kN
= F / A
( ) 2
20
=
25kN /
4
=0.08 kN/mm 2
NHO JKA PSAS Page 3