Page 2 - Lippincott's Visual Nursing_ A Guide to Diseases, Skills, and Treatmentspo_Neat
P. 2
LWBK942-C02[11-76].qxd 6/27/11 8:38 PM Page 18
18 Cardiovascular care
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the Primary cardiomyopathy refers to CARDIOMYOPATHY,
heart where the heart muscle tissue changes in the heart muscle without a DILATED
can’t work properly or as efficiently specific cause. Secondary cardiomy- Dilated cardiomyopathy results from
as it should. Cardiomyopathy can be opathy results from disorders that in-
extensively damaged myocardial mus-
classified as primary or secondary. volve other organs as well as the heart. cle fibers. This disorder interferes
There are four types of cardiomy-
with myocardial metabolism and
opathy—dilated, restrictive, hyper- grossly dilates all four chambers of the
trophic, and arrhythmogenic right
heart, giving the heart a globular ap-
ventricular dysplasia. Dilated or con- pearance and shape. It usually isn’t
How dilated gestive cardiomyopathy (most com- diagnosed until it has reached an ad-
mon) and restrictive cardiomyopathy
cardiomyopathy are discussed here. vanced stage, and the prognosis is
happens generally poor.
Myocardial muscle fibers are
extensively damaged. PICTURING
PATHO
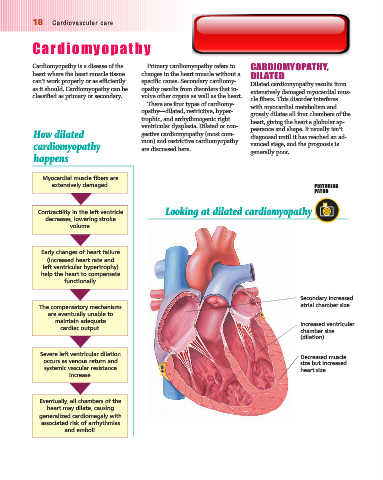
Contractility in the left ventricle Looking at dilated cardiomyopathy
decreases, lowering stroke
volume.
Early changes of heart failure
(increased heart rate and
left ventricular hypertrophy)
help the heart to compensate
functionally.
Secondary increased
atrial chamber size
The compensatory mechanisms
are eventually unable to
maintain adequate Increased ventricular
cardiac output. chamber size
(dilation)
Severe left ventricular dilation Decreased muscle
occurs as venous return and size but increased
systemic vascular resistance heart size
increase.
Eventually, all chambers of the
heart may dilate, causing
generalized cardiomegaly with
associated risk of arrhythmias
and emboli.