Page 21 - HSoS_V3_30-5-23
P. 21
15
sketching styles
Product Design
is to indicate human scale or to show human positioning in relation to
There are many ways the human can be presented through sketching but
Design in Carlow focuses on ‘humanising innovation’. When sketching it
ÇÖ¡¬®èʼn̺ʼnyÌʼnµºÒʼnÒºʼn¡µÒÈÈÖÅÒʼnÒ ʼnÒ ºÖ ÒʼnăºâĜʼnʼnY ʼnÅÖÈźÌʼnyÒʼnÒ ¡ÌʼnÌÒyʼn
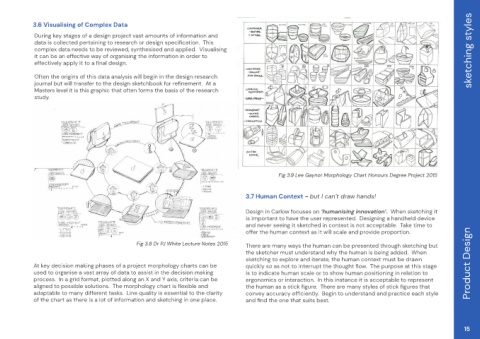
Fig 3.9 Lee Gaynor Morphology Chart Honours Degree Project 2015
is important to have the user represented. Designing a handheld device
ergonomics or interaction. In this instance it is acceptable to represent
and never seeing it sketched in context is not acceptable. Take time to
Ò ʼn Ö´yµʼnyÌʼnyʼnÌÒ¡¬ʼnĂÖÈĜʼnʼnY ÈʼnyÈʼn´yµèʼnÌÒè®ÌʼnºʼnÌÒ¡¬ʼnĂÖÈÌʼnÒ yÒʼn
the sketcher must understand why the human is being added. When
sketching to explore and iterate, the human context must be drawn
offer the human context as it will scale and provide proportion.
3.7 Human Context - but I can’t draw hands!
yµʼnõʼnÒ ʼnºµʼnÒ yÒʼnÌÖ¡ÒÌʼn
ÌÒĜ ºµáèʼnyÖÈyèʼnĂ¡µÒ®èĜʼnʼn ¡µʼnÒºʼnÖµÈÌÒyµʼnyµʼnÅÈyÒ¡ʼny ʼnÌÒè®ʼn
complex data needs to be reviewed, synthesised and applied. Visualising
Fig 3.8 Dr PJ White Lecture Notes 2015
3.6 Visualising of Complex Data During key stages of a design project vast amounts of information and yÒyʼn¡Ìʼnº®®ÒʼnÅÈÒy¡µ¡µʼnÒºʼnÈÌyÈ ʼnºÈʼnÌ¡µʼnÌÅ¡ĂyÒ¡ºµĜʼnʼnY ¡Ìʼn it can be an effective way of organising the information in order to Ò¡á®èʼnyÅÅ®èʼn¡ÒʼnÒºʼnyʼnõy®ʼnÌ¡µĜ Often the origins of this data analysis will begin in the design research «ºÖȵy®ʼn
ÖÒʼnâ¡®®ʼnÒÈyµÌÈʼnÒºʼnÒ ʼnÌ¡µʼn̬Ò
ºº¬ʼnºÈʼnÈõ´µÒĜʼnʼn Òʼnyʼn Masters level it is this graphic t