Page 72 - Lab Manual & Project class 12
P. 72
LABORATORY MANUAL CHEMISTRY
This yellow precipitate (PbI ) is soluble in boiling water and reappears
2
on cooling as shining crystals.
2. On addition of potassium chromate (K CrO ) solution a yellow precipitate
4
2
of lead chromate is obtained. This confirms the presence of Pb ions.
2+
PbCl + K CrO 4 PbCrO + 2KCl
2
2
4
(Hot solution) Lead chromate
(Yellow precipitate)
The yellow precipitate (PbCrO ) is soluble in hot NaOH solution.
4
PbCrO + 4NaOH Na [Pb(OH) ] + Na CrO
4 2 4 2 4
Sodium tetra
hydroxoplumbate (II)
3. A white precipitate of lead sulphate (PbSO ) is formed on addition of
4
Maxbrain Chemistry
alcohol followed by dil. H SO .
2 4
PbCl + H SO PbSO + 2 HCl
2 2 4 4
Lead sulphate
(White precipitate)
Lead sulphate is soluble in ammonium acetate solution due to the formation
of tetraacetoplumbate(II) ions. This reaction may be promoted by addition of few
drops of acetic acid.
Hydrogen PbSO + 4 CH COONH 4 (NH ) [Pb(CH COO) ] + (NH ) SO 4
4
3
3
4 2
4 2
4
sulphide Ammonium
tetraacetoplumbate(II)
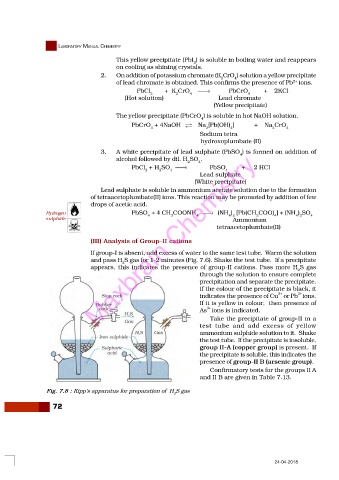
(III) Analysis of Group–II cations
If group-I is absent, add excess of water to the same test tube. Warm the solution
and pass H S gas for 1-2 minutes (Fig. 7.6). Shake the test tube. If a precipitate
2
appears, this indicates the presence of group-II cations. Pass more H S gas
2
through the solution to ensure complete
precipitation and separate the precipitate.
If the colour of the precipitate is black, it
2+
2+
indicates the presence of Cu or Pb ions.
If it is yellow in colour, then presence of
3+
As ions is indicated.
Take the precipitate of group-II in a
test tube and add excess of yellow
ammonium sulphide solution to it. Shake
the test tube. If the precipitate is insoluble,
group II-A (copper group) is present. If
the precipitate is soluble, this indicates the
presence of group-II B (arsenic group).
Confirmatory tests for the groups II A
and II B are given in Table 7.13.
Fig. 7.8 : Kipp’s apparatus for preparation of H S gas
2
72
24-04-2018