Page 97 - Lab Manual & Project class 12
P. 97
Organic compounds containing amino group are basic in nature.
Thus they easily react with acids to form salts, which are soluble
in water.
Both, aliphatic and aromatic amines are classified into three
classes namely– primary(–NH ), secondary(-NH-) and tertiary (-N<),
2
depending upon the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the
nitrogen atom. Primary amine has two hydrogen atoms, secondary
has one while tertiary amine has no hydrogen atom attached to
nitrogen.
(i) Carbylamine test
Aliphatic as well as aromatic primary amines give carbylamine test
in which an amine is heated with chloroform.
∆
R-NH + CHCl + 3KOH → RNC + 3KCl + 3H O
2 3 2
(R=alkyl or aryl group) (Carbylamine)
Maxbrain Chemistry
Carbylamine so formed is highly toxic and should be destroyed
immediately after the test. For this cool the test tube and add
carefully an excess of conc. HCl.
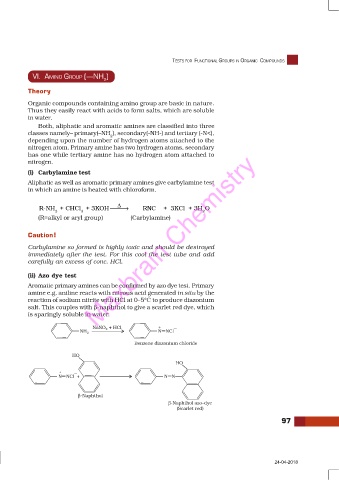
(ii) Azo dye test
Aromatic primary amines can be confirmed by azo dye test. Primary
amine e.g. aniline reacts with nitrous acid generated in situ by the
reaction of sodium nitrite with HCl at 0–5°C to produce diazonium
salt. This couples with β-naphthol to give a scarlet red dye, which
is sparingly soluble in water.
24-04-2018