Page 14 - e-Learning Modul Based on ESD
P. 14
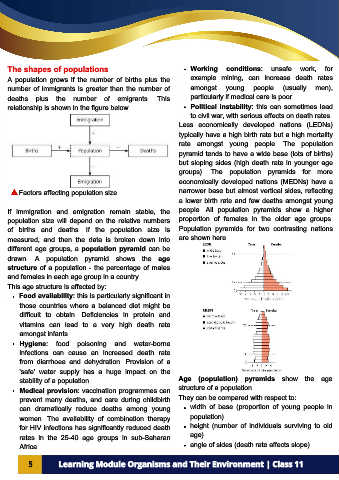
The shapes of populations Working conditions: unsafe work, for
A population grows if the number of births plus the example mining, can increase death rates
number of immigrants is greater than the number of amongst young people (usually men),
deaths plus the number of emigrants. This particularly if medical care is poor.
relationship is shown in the figure below. Political instability: this can sometimes lead
to civil war, with serious effects on death rates.
Less economically developed nations (LEDNs)
typically have a high birth rate but a high mortality
rate amongst young people. The population
pyramid tends to have a wide base (lots of births)
but sloping sides (high death rate in younger age
groups). The population pyramids for more
economically developed nations (MEDNs) have a
Factors affecting population size narrower base but almost vertical sides, reflecting
a lower birth rate and few deaths amongst young
If immigration and emigration remain stable, the people. All population pyramids show a higher
population size will depend on the relative numbers proportion of females in the older age groups.
of births and deaths. If the population size is Population pyramids for two contrasting nations
measured, and then the data is broken down into are shown here.
different age groups, a population pyramid can be
drawn. A population pyramid shows the age
structure of a population - the percentage of males
and females in each age group in a country.
This age structure is affected by:
Food availability: this is particularly significant in
those countries where a balanced diet might be
difficult to obtain. Deficiencies in protein and
vitamins can lead to a very high death rate
amongst infants.
Hygiene: food poisoning and water-borne
infections can cause an increased death rate
from diarrhoea and dehydration. Provision of a
'safe' water supply has a huge impact on the
stability of a population. Age (population) pyramids show the age
Medical provision: vaccination programmes can structure of a population.
prevent many deaths, and care during childbirth They can be compared with respect to:
can dramatically reduce deaths among young width of base (proportion of young people in
women. The availability of combination therapy population)
for HIV infections has significantly reduced death height (number of individuals surviving to old
rates in the 25-40 age groups in sub-Saharan age)
Africa. angle of sides (death rate affects slope).
5 Learning Module Organisms and Their Environment | Class 11