Page 21 - DP Digital Sample
P. 21
innumerable clinical applications which are conservative.
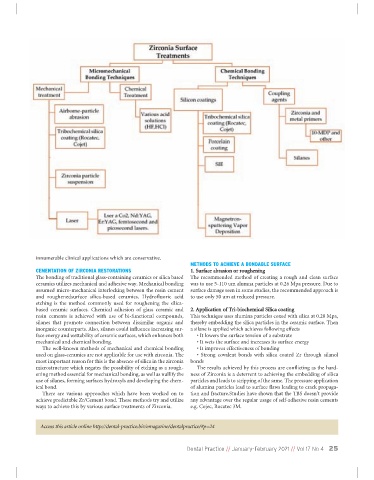
METHODS TO ACHIEVE A BONDABLE SURFACE
CEMENTATION OF ZIRCONIA RESTORATIONS 1. Surface abrasion or roughening
The bonding of traditional glass-containing ceramics or silica based The recommended method of creating a rough and clean surface
ceramics utilizes mechanical and adhesive way. Mechanical bonding was to use 5-110 um alumna particles at 0.26 Mpa pressure. Due to
assumed micro-mechanical interlocking between the resin cement surface damage seen in some studies, the recommended approach is
and roughenedsurface silica-based ceramics. Hydrofluoric acid to use only 50 um at reduced pressure.
etching is the method commonly used for roughening the silica-
based ceramic surfaces. Chemical adhesion of glass ceramic and 2. Application of Tri-biochemical Silica coating
resin cements is achieved with use of bi-functional compounds, This technique uses alumina particles coxed with silica at 0.28 Mpa,
silanes that promote connection between dissimilar organic and thereby embedding the silica particles in the ceramic surface. Then
inorganic counterparts. Also, silanes could influence increasing sur- a silane is applied which achieves following effects
face energy and wettability of ceramic surfaces, which enhances both • It lowers the surface tension of a substrate
mechanical and chemical bonding. • It wets the surface and increases its surface energy
The well-known methods of mechanical and chemical bonding • It improves effectiveness of bonding
used on glass-ceramics are not applicable for use with zirconia. The • Strong covalent bonds with silica coated Zr through silanol
most important reason for this is the absence of silica in the zirconia bonds
microstructure which negates the possibility of etching as a rough- The results achieved by this process are conflicting as the hard-
ening method essential for mechanical bonding, as well as nullify the ness of Zirconia is a deterrent to achieving the embedding of silica
use of silanes, forming surfaces hydroxyls and developing the chem- particles and leads to stripping of the same. The pressure application
ical bond. of alumina particles lead to surface flaws leading to crack propaga-
There are various approaches which have been worked on to tion and fracture.Studies have shown that the TBS doesn’t provide
achieve predictable Zr/Cement bond. These methods try and utilize any advantage over the regular usage of self-adhesive resin cements
ways to achieve this by various surface treatments of Zirconia. e.g. Cojec, Rocatec 3M.
Access this article online http://dental-practice.biz/emagazine/dentalpractice/#p=24
Dental Practice // January-February 2021 // Vol 17 No 4 25