Page 39 - DP Vol 17 No 4 ok
P. 39
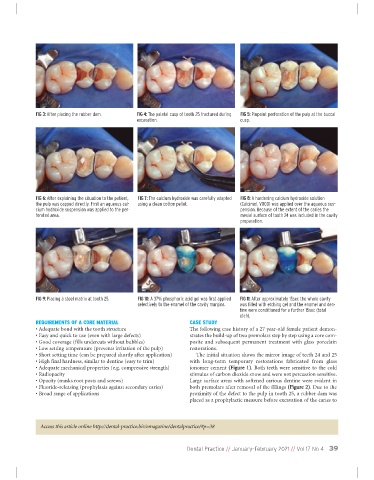
FIG 3: After placing the rubber dam. FIG 4: The palatal cusp of tooth 25 fractured during FIG 5: Pinpoint perforation of the pulp at the buccal
excavation. cusp.
FIG 6: After explaining the situation to the patient, FIG 7: The calcium hydroxide was carefully adapted FIG 8: A hardening calcium hydroxide solution
the pulp was capped directly. First an aqueous cal- using a clean cotton pellet. (Calcimol, VOCO) was applied over the aqueous sus-
cium hydroxide suspension was applied to the per- pension. Because of the extent of the caries the
forated area. mesial surface of tooth 24 was included in the cavity
preparation.
FIG 9: Placing a steel matrix at tooth 25. FIG 10: A 37% phosphoric acid gel was first applied FIG 11: After approximately 15sec the whole cavity
selectively to the enamel of the cavity margins. was filled with etching gel and the enamel and den-
tine were conditioned for a further 15sec (total
etch).
REQUIREMENTS OF A CORE MATERIAL CASE STUDY
• Adequate bond with the tooth structure The following case history of a 27 year-old female patient demon-
• Easy and quick to use (even with large defects) strates the build-up of two premolars step by step using a core com-
• Good coverage (fills undercuts without bubbles) posite and subsequent permanent treatment with glass porcelain
• Low setting temperature (prevents irritation of the pulp) restorations.
• Short setting time (can be prepared shortly after application) The initial situation shows the mirror image of teeth 24 and 25
• High final hardness, similar to dentine (easy to trim) with long-term temporary restorations fabricated from glass
• Adequate mechanical properties (e.g. compressive strength) ionomer cement (Figure 1). Both teeth were sensitive to the cold
• Radiopacity stimulus of carbon dioxide snow and were not percussion sensitive.
• Opacity (masks root posts and screws) Large surface areas with softened carious dentine were evident in
• Fluoride-releasing (prophylaxis against secondary caries) both premolars after removal of the fillings (Figure 2). Due to the
• Broad range of applications proximity of the defect to the pulp in tooth 25, a rubber dam was
placed as a prophylactic measure before excavation of the caries to
Access this article online http://dental-practice.biz/emagazine/dentalpractice/#p=38
Dental Practice // January-February 2021 // Vol 17 No 4 39