Page 7 - المحاضرة 1 و 2
P. 7
Chapter One: Electrostatic
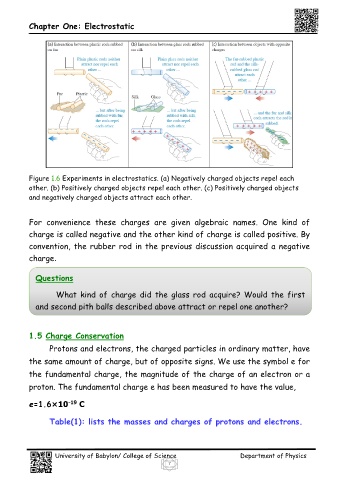
Figure 1.6 Experiments in electrostatics. (a) Negatively charged objects repel each
other. (b) Positively charged objects repel each other. (c) Positively charged objects
and negatively charged objects attract each other.
For convenience these charges are given algebraic names. One kind of
charge is called negative and the other kind of charge is called positive. By
convention, the rubber rod in the previous discussion acquired a negative
charge.
Questions
What kind of charge did the glass rod acquire? Would the first
and second pith balls described above attract or repel one another?
1.5 Charge Conservation
Protons and electrons, the charged particles in ordinary matter, have
the same amount of charge, but of opposite signs. We use the symbol e for
the fundamental charge, the magnitude of the charge of an electron or a
proton. The fundamental charge e has been measured to have the value,
e=1.6×10-19 C
Table(1): lists the masses and charges of protons and electrons.
University of Babylon/ College of Science Department of Physics
7