Page 15 - Practical-organic-3
P. 15
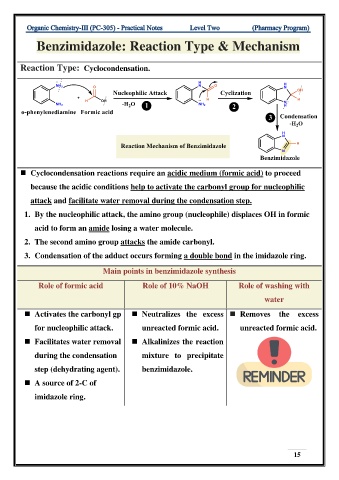
Benzimidazole: Reaction Type & Mechanism
Reaction Type: Cyclocondensation.
◼ Cyclocondensation reactions require an acidic medium (formic acid) to proceed
because the acidic conditions help to activate the carbonyl group for nucleophilic
attack and facilitate water removal during the condensation step.
1. By the nucleophilic attack, the amino group (nucleophile) displaces OH in formic
acid to form an amide losing a water molecule.
2. The second amino group attacks the amide carbonyl.
3. Condensation of the adduct occurs forming a double bond in the imidazole ring.
Main points in benzimidazole synthesis
Role of formic acid Role of 10% NaOH Role of washing with
water
◼ Activates the carbonyl gp ◼ Neutralizes the excess ◼ Removes the excess
for nucleophilic attack. unreacted formic acid. unreacted formic acid.
◼ Facilitates water removal ◼ Alkalinizes the reaction
during the condensation mixture to precipitate
step (dehydrating agent). benzimidazole.
◼ A source of 2-C of
imidazole ring.
15