Page 18 - Pharmaceutical_Analytical_Chemistry_1_Theoretical_Notes_Level_1
P. 18
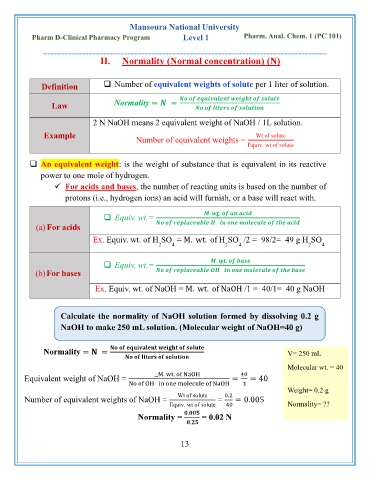
Mansoura National University
Pharm D-Clinical Pharmacy Program Level 1 Pharm. Anal. Chem. 1 (PC 101)
II. Normality (Normal concentration) (N)
Definition ❑ Number of equivalent weights of solute per 1 liter of solution.
Law Normality = =
2 N NaOH means 2 equivalent weight of NaOH / 1L solution.
Example Wt of solute
Number of equivalent weights =
Equiv. wt of solute
❑ An equivalent weight: is the weight of substance that is equivalent in its reactive
power to one mole of hydrogen.
✓ For acids and bases, the number of reacting units is based on the number of
protons (i.e., hydrogen ions) an acid will furnish, or a base will react with.
❑ Equiv. wt.= . .
+
(a) For acids
Ex. Equiv. wt. of H SO = M. wt. of H SO /2 = 98/2= 49 g H SO
2 4 2 4 2 4
−
❑ Equiv. wt.= . .
(b) For bases
Ex. Equiv. wt. of NaOH = M. wt. of NaOH /1 = 40/1= 40 g NaOH
Calculate the normality of NaOH solution formed by dissolving 0.2 g
NaOH to make 250 mL solution. (Molecular weight of NaOH=40 g)
Normality = = V= 250 mL
Molecular wt. = 40
Equivalent weight of NaOH = − M. wt. of NaOH = 40 = 40 g
No of OH in one molecule of NaOH 1
Weight= 0.2 g
Number of equivalent weights of NaOH = Wt of solute = 0.2 = 0.005
Equiv. wt of solute 40 Normality= ??
Normality = . = 0.02 N
.
13