Page 9 - Introduction — Information Literacy and Information Behaviour, Complementary Approaches for Building Capability
P. 9
user
Attracts information
library/system/service
User: information
seeker,
science scholars and
mainly: system/service
oriented, informational
Purpose/s of study
information science
practitioners
Worldwide (limited to
information science
departments)
More theoretical
Context
- Identifying users’
information needs
information needs
developed, related to
- Understanding how
information needs are
- Classifying users
context, and expressed
frameworks, insight
Theoritical outcomes
Theories, models,
Information
needs (IN)
Practical outcome
System & service design
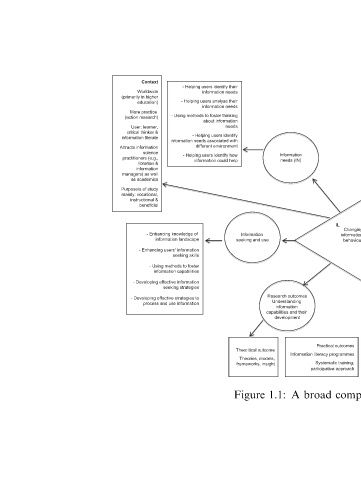
Changing - Understanding users’ information seeking and use Information information patterns/habits seeking and use behaviour IB - Identifying information behaviour Understanding dimension (affective, cognitive, information behavioural) behaviour - Identifying factors that influence people’s info
IL Practical outcomes Information literacy programmes Systematic training, participative approach broad
Information needs (IN) Research outcomes Understanding information capabilities and their development A 1.1:
Information seeking and use Theoritical outcome Theories, models, frameworks, insight Figure
- Helping users identify their information needs - Helping users analyse their information needs - Using methods to foster thinking about information needs - Helping users identify information needs associated with different environment - Helping users identify how information could help seeking skills seeking strate
Context Worldwide (primarily in higher education) More practice (action research) User: learner, critical thinker & information literate Attracts information science practitioners (e.g., librarian & information managers) as well as academics Purpose/s of study mainly: vocational, instructional & beneficial