Page 355 - Physics Coursebook 2015 (A level)
P. 355
Chapter 21: Thermal physics
10 a b
A cylinder of carbon dioxide is at room temperature and at a pressure of 20 atmospheres. A cloth
is placed over the outlet and the tap opened. Solid carbon dioxide is formed on the cloth. Explain,
using the first law of thermodynamics, why the carbon dioxide cools sufficiently for the solid to form. [3] Solid carbon dioxide sublimes to form carbon dioxide gas; that is, it changes directly from a solid to
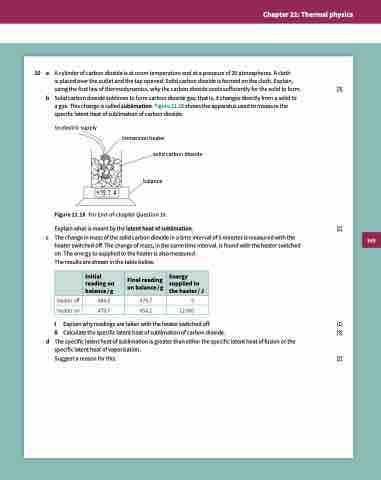
a gas. This change is called sublimation. Figure 21.18 shows the apparatus used to measure the
specific latent heat of sublimation of carbon dioxide.
to electric supply
immersion heater
solid carbon dioxide
balance
g
c
Figure 21.18 For End-of-chapter Question 10.
Explain what is meant by the latent heat of sublimation. [2] The change in mass of the solid carbon dioxide in a time interval of 5 minutes is measured with the
heater switched off. The change of mass, in the same time interval, is found with the heater switched on. The energy to supplied to the heater is also measured.
The results are shown in the table below.
heater off 484.3 479.7 0
heater on 479.7 454.2 12 000
i Explain why readings are taken with the heater switched off. [1]
ii Calculate the specific latent heat of sublimation of carbon dioxide. [3]
The specific latent heat of sublimation is greater than either the specific latent heat of fusion or the
specific latent heat of vaporisation.
Suggest a reason for this. [2]
Initial reading on balance / g
Final reading on balance / g
Energy supplied to the heater / J
d
343