Page 499 - Physics Coursebook 2015 (A level)
P. 499
Chapter 30: Quantum physics
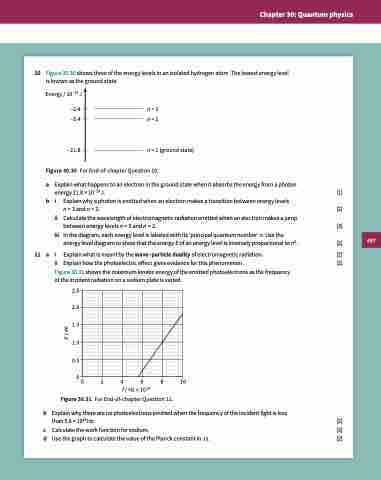
10 Figure 30.30 shows three of the energy levels in an isolated hydrogen atom. The lowest energy level is known as the ground state.
Energy / 10–19 J
–2.4 n = 3
–5.4 n = 2
–21.8 n = 1 (ground state) Figure 30.30 For End-of-chapter Question 10.
a
b i
Explain what happens to an electron in the ground state when it absorbs the energy from a photon
energy 21.8 × 10−19 J. [1]
Explain why a photon is emitted when an electron makes a transition between energy levels
n=3andn=2. [2]
ii Calculate the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation emitted when an electron makes a jump
between energy levels n = 3 and n = 2. [3]
iii Inthediagram,eachenergylevelislabeledwithits‘principalquantumnumber’n.Usethe
energy level diagram to show that the energy E of an energy level is inversely proportional to n2. [2]
Explain what is meant by the wave–particle duality of electromagnetic radiation. [2] Figure 30.31 shows the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons as the frequency
of the incident radiation on a sodium plate is varied.
2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5
00 2 4 6 8 10 f / Hz × 1014
Figure 30.31 For End-of-chapter Question 11.
Explain why there are no photoelectrons emitted when the frequency of the incident light is less
than 5.6 × 1014 Hz. [2] Calculate the work function for sodium. [3] Use the graph to calculate the value of the Planck constant in J s. [2]
11 a i
ii Explain how the photoelectric effect gives evidence for this phenomenon. [2]
b
c d
487
E / eV