Page 493 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 493
2. What is the effect of Mexico’s falling income on the demand for level change on the demand and on the exchange rate, for
money and the nominal interest rate in Mexico? Mexican pesos?
Demand for money Nominal interest rate Demand for pesos Exchange rate
a. increases decreases a. increases appreciates
b. decreases decreases b. increases depreciates
c. increases increases c. decreases appreciates
d. decreases increases d. decreases depreciates
e. increases unchanged e. decreases is unchanged
3. If the aggregate price level in Mexico decreases, what will 5. If the Mexican government pursues expansionary fiscal
happen to the real interest rate? policy in response to the recession, what will happen to
a. It will increase. aggregate demand and aggregate supply in the short-run? Section 8 The Open Economy: International Trade and Finance
b. It will decrease. Aggregate demand Short-run aggregate supply
c. It will be unchanged. a. increase increase
d. It will stabilize. b. increase decrease
e. It cannot be determined. c. decrease increase
d. decrease decrease
4. Suppose the aggregate price level in Mexico decreases relative
e. increase no change
to that in the United States. What is the effect of this price
Tackle the Test: Free-Response Questions
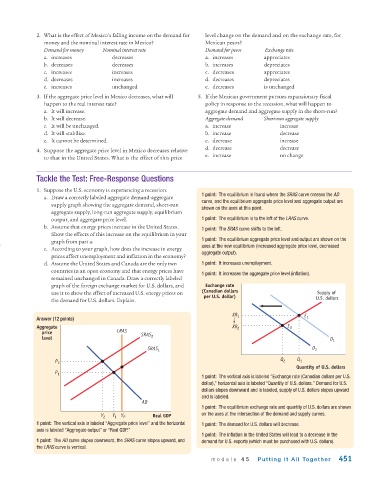
1. Suppose the U.S. economy is experiencing a recession.
1 point: The equilibrium is found where the SRAS curve crosses the AD
a. Draw a correctly labeled aggregate demand-aggregate
curve, and the equilibrium aggregate price level and aggregate output are
supply graph showing the aggregate demand, short-run
shown on the axes at this point.
aggregate supply, long-run aggregate supply, equilibrium
output, and aggregate price level. 1 point: The equilibrium is to the left of the LRAS curve.
b. Assume that energy prices increase in the United States. 1 point: The SRAS curve shifts to the left.
Show the effects of this increase on the equilibrium in your
1 point: The equilibrium aggregate price level and output are shown on the
graph from part a.
axes at the new equilibrium (increased aggregate price level, decreased
c. According to your graph, how does the increase in energy
aggregate output).
prices affect unemployment and inflation in the economy?
d. Assume the United States and Canada are the only two 1 point: It increases unemployment.
countries in an open economy and that energy prices have
1 point: It increases the aggregate price level (inflation).
remained unchanged in Canada. Draw a correctly labeled
graph of the foreign exchange market for U.S. dollars, and Exchange rate
(Canadian dollars
use it to show the effect of increased U.S. energy prices on Supply of
per U.S. dollar) U.S. dollars
the demand for U.S. dollars. Explain.
XR 1 E
Answer (12 points) 1
Aggregate XR 2 E 2
price LRAS SRAS
level 2 D 1
SRAS 1 D 2
P 2 Q 2 Q 1
Quantity of U.S. dollars
P 1
1 point: The vertical axis is labeled “Exchange rate (Canadian dollars per U.S.
dollar),” horizontal axis is labeled “Quantity of U.S. dollars.” Demand for U.S.
dollars slopes downward and is labeled, supply of U.S. dollars slopes upward
and is labeled.
AD
1 point: The equilibrium exchange rate and quantity of U.S. dollars are shown
Y 2 Y 1 Y P Real GDP on the axes at the intersection of the demand and supply curves.
1 point: The vertical axis is labeled “Aggregate price level” and the horizontal 1 point: The demand for U.S. dollars will decrease.
axis is labeled “Aggregate output” or “Real GDP.”
1 point: The inflation in the United States will lead to a decrease in the
1 point: The AD curve slopes downward, the SRAS curve slopes upward, and demand for U.S. exports (which must be purchased with U.S. dollars).
the LRAS curve is vertical.
module 45 Putting It All Together 451