Page 602 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 602
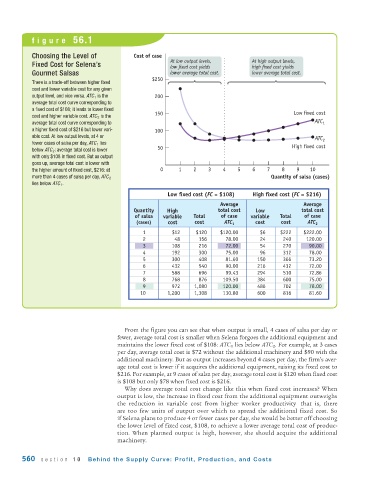
figure 56.1
Choosing the Level of Cost of case
At low output levels, At high output levels,
Fixed Cost for Selena’s low fixed cost yields high fixed cost yields
Gourmet Salsas lower average total cost. lower average total cost.
$250
There is a trade-off between higher fixed
cost and lower variable cost for any given
output level, and vice versa. ATC 1 is the 200
average total cost curve corresponding to
a fixed cost of $108; it leads to lower fixed
cost and higher variable cost. ATC 2 is the 150 Low fixed cost
average total cost curve corresponding to ATC 1
a higher fixed cost of $216 but lower vari- 100
able cost. At low output levels, at 4 or
ATC 2
fewer cases of salsa per day, ATC 1 lies High fixed cost
below ATC 2 : average total cost is lower 50
with only $108 in fixed cost. But as output
goes up, average total cost is lower with
the higher amount of fixed cost, $216: at 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Quantity of salsa (cases)
more than 4 cases of salsa per day, ATC 2
lies below ATC 1 .
Low fixed cost (FC = $108) High fixed cost (FC = $216)
Average Average
Quantity High total cost Low total cost
of salsa variable Total of case variable Total of case
(cases) cost cost ATC 1 cost cost ATC 2
1 $ 12 $ 120 $120.00 $ 6 $222 $222.00
2 48 156 78.00 24 240 120.00
3 108 216 72.00 54 270 90.00
4 192 300 75.00 96 312 78.00
5 300 408 81.60 150 366 73.20
6 432 540 90.00 216 432 72.00
7 588 696 99.43 294 510 72.86
8 768 876 109.50 384 600 75.00
9 972 1,080 120.00 486 702 78.00
10 1,200 1,308 130.80 600 816 81.60
From the figure you can see that when output is small, 4 cases of salsa per day or
fewer, average total cost is smaller when Selena forgoes the additional equipment and
maintains the lower fixed cost of $108: ATC 1 lies below ATC 2 . For example, at 3 cases
per day, average total cost is $72 without the additional machinery and $90 with the
additional machinery. But as output increases beyond 4 cases per day, the firm’s aver-
age total cost is lower if it acquires the additional equipment, raising its fixed cost to
$216. For example, at 9 cases of salsa per day, average total cost is $120 when fixed cost
is $108 but only $78 when fixed cost is $216.
Why does average total cost change like this when fixed cost increases? When
output is low, the increase in fixed cost from the additional equipment outweighs
the reduction in variable cost from higher worker productivity—that is, there
are too few units of output over which to spread the additional fixed cost. So
if Selena plans to produce 4 or fewer cases per day, she would be better off choosing
the lower level of fixed cost, $108, to achieve a lower average total cost of produc-
tion. When planned output is high, however, she should acquire the additional
machinery.
560 section 10 Behind the Supply Curve: Profit, Production, and Costs