Page 892 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 892
S-46 SOLUTIONS TO AP REVIEW QUESTIONS
the marginal social cost—an inefficient outcome. In that rivers and aquifers need to be pumped. The difference
case, allowing an overdue patron another day would between the marginal social benefit and the marginal pri-
increase total social benefit more than it would increase vate benefit to individual homeowners is the marginal
total social cost. So charging a moderate fine that reduces external benefit. A Pigouvian subsidy for installing water-
the number of days that books are returned late to the saving toilets equal to the marginal external benefit could
socially optimal number of days is appropriate. bring the marginal private benefit to individual home-
owners in line with the marginal social benefit.
Tackle the Test: c. Disposing of old computer monitors imposes an external
Multiple-Choice Questions cost: the marginal private cost to those disposing of old
1. a computer monitors is lower than the marginal social
2. a cost, since environmental pollution is borne by people
other than the person disposing of the monitor. The dif-
3. d ference between the marginal social cost and the margin-
4. b al private cost to those disposing of old computer moni-
tors is the marginal external cost. A Pigouvian tax on the
5. d disposal of computer monitors equal to the marginal
Tackle the Test: external cost, or a system of tradable permits for their
disposal, could raise the marginal private cost to those
Free-Response Questions disposing of old computer monitors up to the level of the
marginal social cost.
2. a. The marginal social cost of pollution is the additional cost
imposed on society by an additional unit of pollution. Tackle the Test:
b. The marginal social benefit of pollution is the additional Multiple-Choice Questions
benefit to society from an additional unit of pollution.
Even when a firm could provide the same quantity of 1. a
output without polluting as much, there is a benefit from 2. d
polluting more because the firm can devote less money
and resources to pollution avoidance. 3. c
c. The socially optimal level of pollution is that level at 4. a
which the marginal social benefit of pollution equals the 5.
marginal social cost. a
Tackle the Test:
Module 75 Free-Response Questions
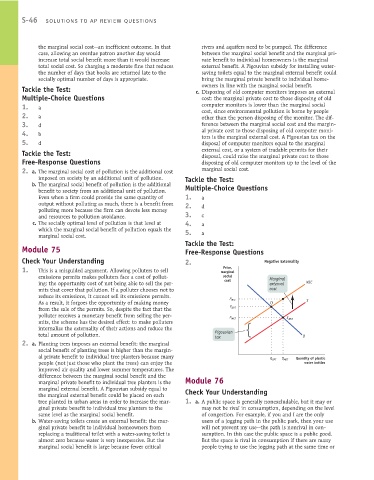
Check Your Understanding 2. Negative Externality
1. This is a misguided argument. Allowing polluters to sell marginal
Price,
emissions permits makes polluters face a cost of pollut- social Marginal
cost
ing: the opportunity cost of not being able to sell the per- external MSC
mits that cover that pollution. If a polluter chooses not to cost
reduce its emissions, it cannot sell its emissions permits.
P MSC S
As a result, it forgoes the opportunity of making money O
from the sale of the permits. So, despite the fact that the P OPT
polluter receives a monetary benefit from selling the per-
P MKT E MKT
mits, the scheme has the desired effect: to make polluters
internalize the externality of their actions and reduce the
Pigouvian
total amount of pollution.
tax D
2. a. Planting trees imposes an external benefit: the marginal
social benefit of planting trees is higher than the margin-
al private benefit to individual tree planters because many Quantity of plastic
Q OPT Q MKT
people (not just those who plant the trees) can enjoy the water bottles
improved air quality and lower summer temperatures. The
difference between the marginal social benefit and the
marginal private benefit to individual tree planters is the Module 76
marginal external benefit. A Pigouvian subsidy equal to Check Your Understanding
the marginal external benefit could be placed on each
tree planted in urban areas in order to increase the mar- 1. a. A public space is generally nonexcludable, but it may or
ginal private benefit to individual tree planters to the may not be rival in consumption, depending on the level
same level as the marginal social benefit. of congestion. For example, if you and I are the only
b. Water-saving toilets create an external benefit: the mar- users of a jogging path in the public park, then your use
ginal private benefit to individual homeowners from will not prevent my use—the path is non rival in con-
replacing a traditional toilet with a water-saving toilet is sumption. In this case the public space is a public good.
almost zero because water is very inexpensive. But the But the space is rival in consumption if there are many
marginal social benefit is large because fewer critical people trying to use the jogging path at the same time or