Page 716 - Geosystems An Introduction to Physical Geography 4th Canadian Edition
P. 716
A-11 Appendix C
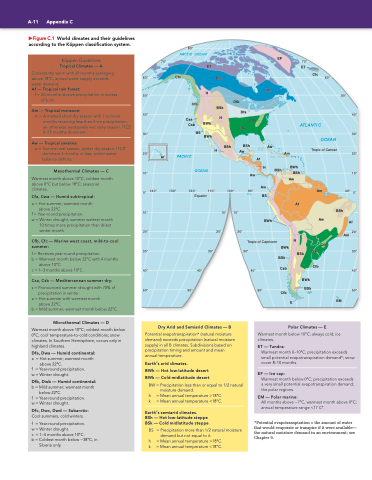
Figure C.1 World climates and their guidelines according to the Köppen classification system.
80°
ARCTIC OCEAN
b
Köppen Guidelines 70°
Tropical Climates — A ET
Consistently warm with all months averaging
above 18°C; annual water supply exceeds 60° Cfc Dfc water demand.
Af — Tropical rain forest:
EF
70°
ET
f = All months receive precipitation in excess 50° H
Dfc
of 6 cm.
Am — Tropical monsoon:
Cfb
Dfb BSk
Dfa
H Cfb
Cfa
BSh BSh Aw
50°
40°
30°
20°
10°
m = A marked short dry season with 1 or more
months receiving less than 6 cm precipitation;
an otherwise excessively wet rainy season. ITCZ
6–12 months dominant. 30° BS BWh
Aw — Tropical savanna:
w = Summer wet season, winter dry season; ITCZ H dominant 6 months or less, winter water- 20°
balance deficits. Af PACIFIC
Mesothermal Climates — C
Warmest month above 10°C; coldest month above 0°C but below 18°C; seasonal climates.
Cfa, Cwa — Humid subtropical:
a = Hot summer; warmest month above 22°C.
f = Year-round precipitation.
w = Winter drought, summer wettest month
10 times more precipitation than driest winter month.
Cfb, Cfc — Marine west coast, mild-to-cool summer:
10°
0° 140° 130°
OCEAN
120° 110°
H
Aw BS
BSh
BWh BSh
f = Receives year-round precipitation. 30° b = Warmest month below 22°C with 4 months
above 10°C.
c = 1–3 months above 10°C. 40°
Csa, Csb — Mediterranean summer dry:
s = Pronounced summer drought with 70% of 50° precipitation in winter.
a = Hot summer with warmest month above 22°C.
b = Mild summer; warmest month below 22°C.
Microthermal Climates — D
Warmest month above 10°C; coldest month below 0°C; cool temperature-to-cold conditions; snow
30°
30°
BWk BSk
Csb
Cfb
BSk
Cfa Cfb
demand) exceeds precipitation (natural moisture highland climates. supply) in all B climates. Subdivisions based on
Dfa, Dwa — Humid continental: precipitation timing and amount and mean
a = Hot summer; warmest month annual temperature. above 22°C. Earth’s arid climates.
Warmest month below 10°C; always cold; ice climates.
ET — Tundra:
climates. In Southern Hemisphere, occurs only in
f = Year-round precipitation. w = Winter drought.
Dfb, Dwb — Humid continental:
b = Mild summer; warmest month below 22°C.
f = Year-round precipitation. w = Winter drought.
Dfc, Dwc, Dwd — Subarctic:
w = Winter drought.
c = 1–4 months above 10°C.
b = Coldest month below −38°C, in
Siberia only.
BWh — Hot low-latitude desert BWk — Cold midlatitude desert
Warmest month 0–10°C; precipitation exceeds small potential evapotranspiration demand*; snow cover 8–10 months.
EF — Ice cap:
Warmest month below 0°C; precipitation exceeds a very small potential evapotranspiration demand; the polar regions.
EM — Polar marine:
All months above −7°C, warmest month above 0°C; annual temperature range <17 C°.
BW = Precipitation less than or equal to 1/2 natural moisture demand.
h = Mean annual temperature >18°C. k = Mean annual temperature <18°C.
Earth’s semiarid climates.
BSh — Hot low-latitude steppe f = Year-round precipitation. BSk — Cold midlatitude steppe
Cool summers, cold winters.
40°
10°
20°
10°
20°
10°
Csa
Csb BWk
ATLANTI C
OCEA N
Tropic of Cancer
Am
Dry Arid and Semiarid Climates — B
Potential evapotranspiration* (natural moisture
Polar Climates — E
Equator
40°
50°
40°
50°
BWk BSk
BS = Precipitation more than 1/2 natural moisture demand but not equal to it.
h = Mean annual temperature >18°C. k = Mean annual temperature <18°C.
*Potential evapotranspiration = the amount of water that would evaporate or transpire if it were available— the natural moisture demand in an environment; see Chapter 9.
100°
Aw
90°
Aw
Af
40° 0°
BSh
Af
20°
Am Cfb
EM
20°
30°
40°
50°
Af
Tropic of Capricorn
H
Aw
BWh
Aw
Am
E
Cfc
60°