Page 434 - The Principle of Economics
P. 434
442 PART SIX
THE ECONOMICS OF LABOR MARKETS
poverty rate
the percentage of the population whose family income falls below an absolute level called the poverty line
poverty line
an absolute level of income set by the federal government for each family size below which a family is deemed to be in poverty
are ranked from the most equal to the most unequal. On the top of the list is Germany, where the richest fifth of the population has income only about 4 times that of the poorest fifth. On the bottom of the list is Brazil, where the richest fifth has income about 25 times that of the poorest fifth. Although all countries have substantial inequality in income, the degree of inequality is not the same everywhere.
When countries are ranked by inequality, the United States ends up slightly behind the middle of the pack. Compared to other economically advanced countries, such as Germany and Canada, the United States has substantial in- equality. But the United States has a more equal income distribution than many developing countries, such as Chile and Brazil.
THE POVERTY RATE
A commonly used gauge of the distribution of income is the poverty rate. The poverty rate is the percentage of the population whose family income falls below an absolute level called the poverty line. The poverty line is set by the federal gov- ernment at roughly three times the cost of providing an adequate diet. This line is adjusted every year to account for changes in the level of prices, and it depends on family size.
To get some idea about what the poverty rate tells us, consider the data for 1998. In that year, the median family had an income of $47,469, and the poverty line for a family of four was $16,660. The poverty rate was 12.7 percent. In other words, 12.7 percent of the population were members of families with incomes be- low the poverty line for their family size.
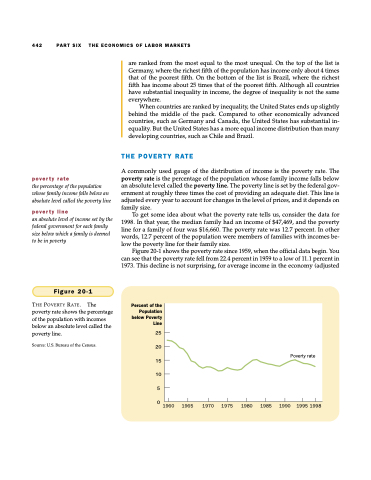
Figure 20-1 shows the poverty rate since 1959, when the official data begin. You can see that the poverty rate fell from 22.4 percent in 1959 to a low of 11.1 percent in 1973. This decline is not surprising, for average income in the economy (adjusted
Figure 20-1
THE POVERTY RATE. The Percent of the
Poverty rate
poverty rate shows the percentage of the population with incomes below an absolute level called the poverty line.
Source: U.S. Bureau of the Census.
Population below Poverty Line
25 20 15 10 5 0
1960 1965
1970 1975
1980 1985 1990
1995 1998