Page 80 - The Principle of Economics
P. 80
80 PART TWO
SUPPLY AND DEMAND I: HOW MARKETS WORK
equilibrium
a situation in which supply and demand have been brought into balance
equilibrium price
the price that balances supply and demand
equilibrium quantity
the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded when the price has adjusted to balance supply and demand
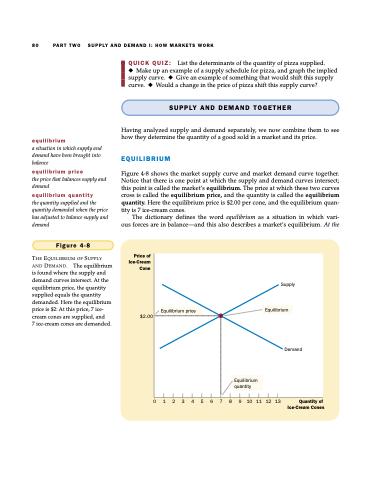
Figure 4-8
THE EQUILIBRIUM OF SUPPLY AND DEMAND. The equilibrium is found where the supply and demand curves intersect. At the equilibrium price, the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. Here the equilibrium price is $2: At this price, 7 ice- cream cones are supplied, and
7 ice-cream cones are demanded.
QUICK QUIZ: List the determinants of the quantity of pizza supplied.
N Make up an example of a supply schedule for pizza, and graph the implied supply curve. N Give an example of something that would shift this supply curve. N Would a change in the price of pizza shift this supply curve?
SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER
Having analyzed supply and demand separately, we now combine them to see how they determine the quantity of a good sold in a market and its price.
EQUILIBRIUM
Figure 4-8 shows the market supply curve and market demand curve together. Notice that there is one point at which the supply and demand curves intersect; this point is called the market’s equilibrium. The price at which these two curves cross is called the equilibrium price, and the quantity is called the equilibrium quantity. Here the equilibrium price is $2.00 per cone, and the equilibrium quan- tity is 7 ice-cream cones.
The dictionary defines the word equilibrium as a situation in which vari- ous forces are in balance—and this also describes a market’s equilibrium. At the
Supply
Equilibrium
Demand
Equilibrium quantity
Equilibrium price
Price of Ice-Cream Cone
$2.00
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Quantityof Ice-Cream Cones