Page 4 - Investigating the Employment of Metacognitive Strategies in Listening Comprehension among Non-Iranian Language Learners
P. 4
Journal of English Language Teaching and Learning, 13 (28) / Fall and Winter 2021, pp 261-277 264
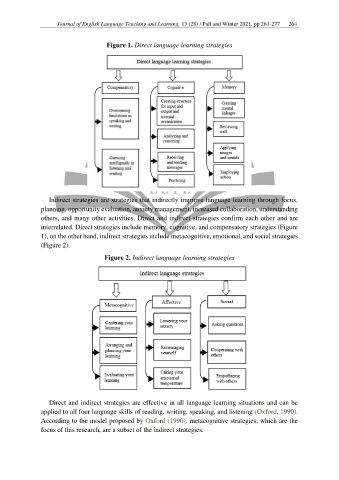
Figure 1. Direct language learning strategies
Indirect strategies are strategies that indirectly improve language learning through focus,
planning, opportunity evaluation, anxiety management, increased collaboration, understanding
others, and many other activities. Direct and indirect strategies confirm each other and are
interrelated. Direct strategies include memory, cognitive, and compensatory strategies (Figure
1), on the other hand, indirect strategies include metacognitive, emotional, and social strategies
(Figure 2).
Figure 2. Indirect language learning strategies
Direct and indirect strategies are effective in all language learning situations and can be
applied to all four language skills of reading, writing, speaking, and listening (Oxford, 1990).
According to the model proposed by Oxford (1990), metacognitive strategies, which are the
focus of this research, are a subset of the indirect strategies.