Page 11 - Algebra
P. 11
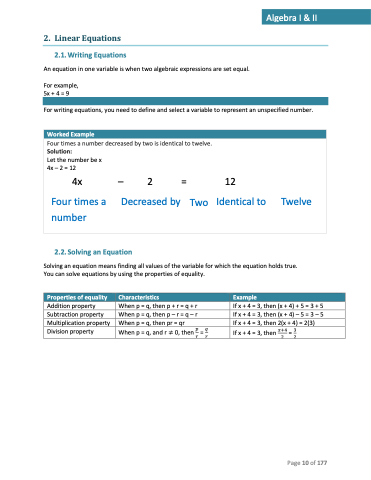
2. Linear Equations
2.1. Writing Equations
An equation in one variable is when two algebraic expressions are set equal.
For example, 5x + 4 = 9
For writing equations, you need to define and select a variable to represent an unspecified number.
Worked Example
Four times a number decreased by two is identical to twelve.
Solution:
Let the number be x 4x – 2 = 12
4x – 2 = 12
Four times a Decreased by Two Identical to Twelve number
2.2. Solving an Equation
Solving an equation means finding all values of the variable for which the equation holds true. You can solve equations by using the properties of equality.
Properties of equality
Characteristics
Example
Addition property Subtraction property Multiplication property Division property
When p = q, then p + r = q + r If x + 4 = 3, then (x + 4) + 5 = 3 + 5 When p = q, then p – r = q – r If x + 4 = 3, then (x + 4) – 5 = 3 – 5 When p = q, then pr = qr If x + 4 = 3, then 2(x + 4) = 2(3)
When p = q, and r ≠ 0, then 𝑝 = 𝑞 𝑟𝑟
If x + 4 = 3, then 𝑥+4 = 3 22
Page 10 of 177
Algebra I & II