Page 120 - ASOP ROT Study Guide
P. 120
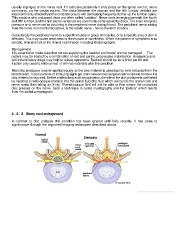
usually impinges on the nerve root. If it extrudes posteriorly it may press on the spinal cord or, more
commonly, on the cauda equina. The discs between the sacrum and the fifth lumbar vertebra are
most commonly affected and the condition occurs with decreasing frequency further up the lumbar spine.
This explains why prolapsed discs are often called "sciatica". Nerve roots emerging beneath the fourth
and fifth lumbar, and the first sacral vertebrae are commonly compressed by discs. The brain interprets
pressure on a nerve root as occurring in the peripheral nerve arising from it. The peripheral nerve arising
from the nerve root mentioned above, is the sciatic nerve - hence the term sciatica.
Occasionally the peripheral nerve to a specific muscle or group of muscles, or to a specific area of skin is
affected. This may cause weakness in the muscle or numbness. When the pattern of symptoms is so
specific, clinicians talk of the clinical examination revealing localizing signs.
Management
It is essential to make sure that nerves supplying the bladder and bowel are not damaged. The
patient may be treated by a combination of rest and gentle, progressive mobilisation. Analgesics and
anti-inflammatory drugs may help to relieve symptoms. Bedrest should be for a short period and
traction only used to enforce rest - it will not materially alter the condition.
Most disc prolapses recover spontaneously as the disc material is absorbed by cells released from the
bloodstream. If pain persists or localizing signs get more severe then surgical intervention to remove the
disc material is required. Before undertaking such an operation, the site of the disc prolapse is confirmed
by injecting a radio-opaque material into the spinal fluid (the fluid which surrounds the spinal cord and
nerve roots) then taking an X-ray. Theradiopaque fluid will not be able to flow where the prolapsed
disc presses on the nerve. Such a technique is called myelography and the "picture" which results
from it is called a myelogram.
4 . 2 . 2 Bony root entrapment
In contrast to disc prolapse this condition has been ignored until fairly recently. It has come to
significance through the improved imaging techniques described above.
http://www.mayfieldclinic.com/PE-STEN.htm