Page 14 - ASOP ROT Study Guide
P. 14
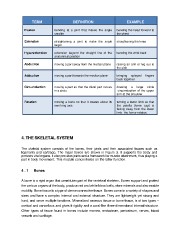
TERM DEFINITION EXAMPLE
Flexion bending at a joint that makes the angle bending the head forward to
Extension
Hyperextension smaller the chest
Abduction
Adduction straightening a joint to make the angle straightening the knee
Circumduction larger
Rotation extension beyond the straight line of the bending the wrist back
anatomical position
moving a part away from the median plane raising an arm or leg out to
the side
moving a part towards the median plane bringing splayed fingers
back together
moving a part so that the distal part moves drawing a large circle
in a circle -circumduction of the upper
arm at the shoulder
moving a bone so that it rotates about its turning a lower limb so that
own long axis the patella (knee cap) is
facing away from the lower
limb -the femur rotates
4. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
The skeletal system consists of the bones, their joints and their associated tissues such as
ligaments and cartilage. The major bones are shown in Figure 3. It supports the body and
protects vital organs. It also provides joints and a framework for muscle attachment, thus playing a
part in body movement. This module concentrates on the latter function.
4 . 1 Bones
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the vertebral skeleton. Bones support and protect
the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals and also enable
mobility. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue. Bones come in a variety of shapes and
sizes and have a complex internal and external structure. They are lightweight yet strong and
hard, and serve multiple functions. Mineralized osseous tissue or bone tissue, is of two types –
cortical and cancellous and gives it rigidity and a coral-like three-dimensional internal structure.
Other types of tissue found in bones include marrow, endosteum, periosteum, nerves, blood
vessels and cartilage.