Page 83 - ASOP ROT Study Guide
P. 83
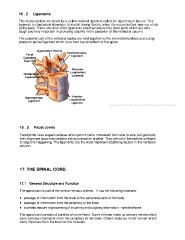
16 . 2 Ligaments
The neural arches are joined by a yellow-colored ligament called the ligamentum flavum. This
ligament is elasticated allowing it to stretch during flexion, when the neural arches open up a little
at the back. There are other short ligaments attached around the facet joints which are very
tough and very important in providing stability in the posterior of the vertebral column.
The posterior part of the vertebral bodies are held together by the intervertebral discs and a long
posterior spinal ligament which runs from top to bottom of the spine.
http://www.coloradospineinstitute.com/subject.php?pn=anatomy-ligaments-
17
.
16 . 3 Facet Joints
Facet joints have sloped surfaces which permit some movement from side to side, but generally
their alignment stops one vertebra sliding forward on another. They are not in themselves sufficient
to stop this happening. The ligaments are the most important stabilizing factors in the vertebral
column.
17. THE SPINAL CORD
17.1 General Structure and Function
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system. It has the following functions:
♦ passage of information from the brain to the peripheral parts of the body
♦ passage of information from the periphery to the brain
♦ a certain amount of processing of incoming and outgoing information - spinal reflexes
The spinal cord consists of bundles of nerve fibers. Some of these make up sensory nerves which
carry sensory information from the periphery to the brain. Others make up motor nerves which
carry impulses from the brain to the muscles.