Page 276 - C:\Users\cbaro\OneDrive\Documents\Flip PDF Professional\Study Guide for the Orthopaedic Technology Certification Exams\
P. 276
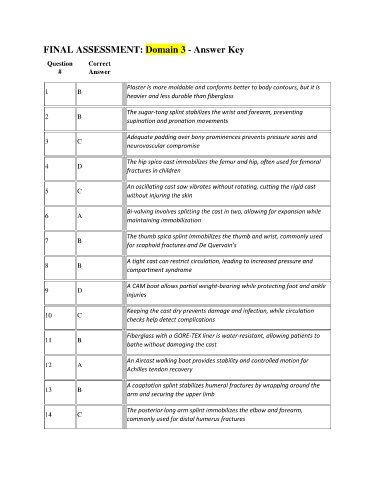
FINAL ASSESSMENT: Domain 3 - Answer Key
Question Correct
# Answer
Plaster is more moldable and conforms better to body contours, but it is
1 B
heavier and less durable than fiberglass
The sugar-tong splint stabilizes the wrist and forearm, preventing
2 B
supination and pronation movements
Adequate padding over bony prominences prevents pressure sores and
3 C
neurovascular compromise
The hip spica cast immobilizes the femur and hip, often used for femoral
4 D
fractures in children
An oscillating cast saw vibrates without rotating, cutting the rigid cast
5 C
without injuring the skin
Bi-valving involves splitting the cast in two, allowing for expansion while
6 A
maintaining immobilization
The thumb spica splint immobilizes the thumb and wrist, commonly used
7 B
for scaphoid fractures and De Quervain's
A tight cast can restrict circulation, leading to increased pressure and
8 B
compartment syndrome
A CAM boot allows partial weight-bearing while protecting foot and ankle
9 D
injuries
Keeping the cast dry prevents damage and infection, while circulation
10 C
checks help detect complications
Fiberglass with a GORE-TEX liner is water-resistant, allowing patients to
11 B
bathe without damaging the cast
An Aircast walking boot provides stability and controlled motion for
12 A
Achilles tendon recovery
A coaptation splint stabilizes humeral fractures by wrapping around the
13 B
arm and securing the upper limb
The posterior long arm splint immobilizes the elbow and forearm,
14 C
commonly used for distal humerus fractures