Page 8 - expanded flexplan brochure
P. 8
Do you really want Poor asset allocation and doing it yourself Get professional management
can lead to subpar investor returns
to go it alone—again? Summary of Investor Returns as of 12/31/15* vs. S&P 500 and Barclays Aggregate Bond Index using your retirement plan’s
12% 10.35% best-kept secret
10% Did you know that by using the managed With help from Flexible Plan Investments and
BE AR MAR KET FACTS account option that is already a part of your your financial adviser, you can use this option
8% 6.73% workplace retirement plan you can unlock a to add a dynamically risk-managed separate
Mathematics of
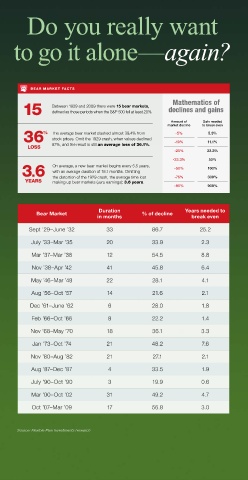
15 Between 1929 and 2009 there were 15 bear markets, declines and gains 6% 3.66% new world of investment choices beyond the account to your workplace retirement
basic core and target-date investments offered
account. This separate account provides a
defined as those periods when the S&P 500 fell at least 20%.
Amount of Gain needed Annualized Return % 4% by the standard workplace retirement plan— gateway to the same management styles as
market decline to break even 1.65% and a professional team that includes your high-net-worth investors, institutions, and
36 % The average bear market slashed almost 39.4% from -5% 5.3% 2% 0.59% financial adviser to help you manage it all? foundations, giving you more tools and
stock prices. Omit the 1929 crash, when values declined
LOSS 87%, and the result is still an average loss of 36.1%. -10% 11.1% 0% Average Equity S&P 500 ® Average Fixed- Barclays Average Asset professional guidance to help your reach
-25% 33.3% Fund Investor Income Investor Aggregate Allocation Fund your retirement funding goals.
-33.3% 50% Over a 30-year span. Bond Index Investor
3.6 On average, a new bear market begins every 5.5 years, -50% 100% IMPORTANT DISCLOSURES Data Sources: Investment Company Institute, Standard & Poor’s, Barclays Capital Index Products and the Bureau of Create a managed
Labor Statistics Average stock investor, average fixed income investor, and average asset allocation investor performance results are calculated using
with an average duration of 18.1 months. Omitting
redemptions, and exchanges. This method of calculation captures realized and unrealized capital gains, dividends, interest, trading costs, sales
YEARS the distortion of the 1929 crash, the average time lost -75% 300% data supplied by the Investment Company Institute. Investor returns are represented by the change in total mutual fund assets after excluding sales, workplace retirement Workplace retirement plan
making up bear markets (zero earnings): 3.6 years.
-90% 900% charges, fees, expenses, and any other costs. After calculating investor returns in dollar terms, two percentages are calculated for the period
examined: Total investor return rate and annualized investor return rate. Total return rate is determined by calculating the investor return dollars as a
percentage of the net of the sales, redemptions, and exchanges for each period. The equity market is represented by the Standard & Poor’s 500, an account in 3 easy steps
unmanaged index of common stock. The fixed income market is represented by the Barclays Aggregate Bond Index. Indexes do not take into account
the fees and expenses associated with investing, and individuals cannot invest directly in any index. Past performance cannot guarantee future results.
Duration Years needed to
Bear Market % of decline Self-directed
in months break even STEP 1 brokerage
How can a professional Core investments
account
Sept ’29–June ’32 33 86.7 25.2 financial adviser help You open a self-directed investments (limited)
July ’33–Mar ’35 20 33.9 2.3 me with my workplace brokerage account (SDBA). (full options)
retirement plan?
Mar ’37–Mar ’38 12 54.5 8.8
Nov ’38–Apr ’42 41 45.8 6.4 STEP 2 Work with your trusted adviser
With a trusted adviser’s help,
May ’46–Mar ’48 22 28.1 4.1 here’s what you can expect:
• A knowledgeable and
Aug ’56–Oct ’57 14 21.6 2.1
understanding advocate.
Dec ’61–June ’62 6 28.0 1.8 • Someone to help you determine STEP 3
appropriate dynamic risk-
Feb ’66–Oct ’66 8 22.2 1.4 You partner with Flexible Plan You complete the suitability
managed strategies for you Investments to gain access
Nov ’68–May ’70 18 36.1 3.3 based on your expressed goals, to turnkey, risk-managed questionnaire and investment
management agreement
risk tolerance, time horizon, investment solutions.
Jan ’73–Oct ’74 21 48.2 7.6 and financial situation.
• Peace of mind.
Nov ’80–Aug ’82 21 27.1 2.1 Benefits of the SDBA option Benefits of the core option
Aug ’87–Dec ’87 4 33.5 1.9 • Help with managing your workplace Dynamic risk management from
retirement account before the plan Flexible Plan Investments.
July ’90–Oct ’90 3 19.9 0.6
rolls over, giving you more time to • Within each actively managed
Mar ’00–Oct ’02 31 49.2 4.7 benefit from professional guidance. Quantified mutual fund.
• Dynamic risk management from
Oct ’07–Mar ’09 17 56.8 3.0 • Among the funds used in each
Flexible Plan Investments. QFC strategy.
• You pay no direct advisory fees after • Between the QFC Strategies.
affilated fund credits.
Source: Flexible Plan Investments research
• Many more investment options.
• No trading restrictions.