Page 27 - ANZCP Gazette November 2021
P. 27
2
Perfusion 00(0)
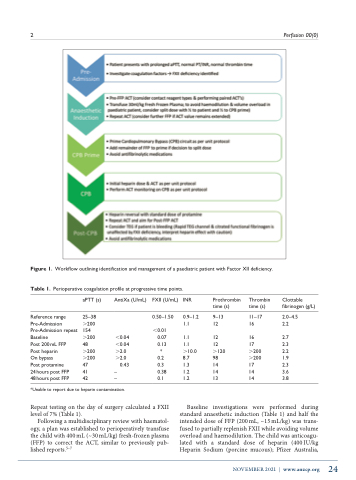
Figure 1. Workflow outlining identification and management of a paediatric patient with Factor XII deficiency.
Table 1. Perioperative coagulation profile at aPTT (s) AntiXa
Reference range 25–38 Pre-Admission >200
Pre-Admission repeat 154
Baseline >200 <0.04 Post 200mL FFP 48 <0.04 Post heparin >200 >2.0 On bypass >200 >2.0 Post protamine 47 0.43 24hours post FFP 41 – 48hours post FFP 42 –
*Unable to report due to heparin contamination.
progressive time points.
(U/mL)
FXII (U/mL)
0.50–1.50
<0.01 0.07 0.13
* 0.2 0.3
0.38 0.1
INR Prothrombin time (s)
0.9–1.2 9–13 1.1 12
1.1 12 1.1 12 >10.0 >120 8.7 98 1.3 14 1.2 14 1.2 13
Thrombin time (s)
11–17 16
16
17 >200 >200 17
14
14
Clottable fibrinogen (g/L)
2.0–4.5 2.2
2.7 2.3 2.2 1.9 2.3 3.6 3.8
Repeat testing on the day of surgery calculated a FXII level of 7% (Table 1).
Following a multidisciplinary review with haematol- ogy, a plan was established to perioperatively transfuse the child with 400 mL (~30 mL/kg) fresh-frozen plasma (FFP) to correct the ACT, similar to previously pub- lished reports.5–7
Baseline investigations were performed during standard anaesthetic induction (Table 1) and half the intended dose of FFP (200 mL, ~15 mL/kg) was trans- fused to partially replenish FXII while avoiding volume overload and haemodilution. The child was anticoagu- lated with a standard dose of heparin (400IU/kg Heparin Sodium (porcine mucous); Pfizer Australia,
NOVEMBER 2021 | www.anzcp.org 24