Page 28 - ANZCP Gazette November 2021
P. 28
Shrimpton et al. 3
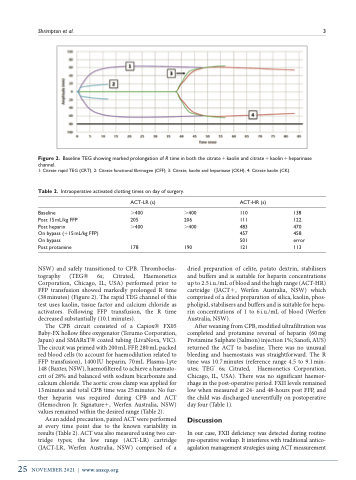
Figure 2. Baseline TEG showing marked prolongation of R time in both the citrate+kaolin and citrate+kaolin+heparinase channel.
1: Citrate rapid TEG (CRT), 2: Citrate functional fibrinogen (CFF), 3: Citrate, kaolin and heparinase (CKH), 4: Citrate kaolin (CK).
Table 2. Intraoperative activated clotting times on day of surgery. ACT-LR (s)
ACT-HR (s)
110 138
111 122
483 470 457 458 501 error 121 113
Baseline
Post 15mL/kg FFP
Post heparin
On bypass (+15mL/kg FFP) On bypass
Post protamine
>400 >400 205 206 >400 >400
178 190
NSW) and safely transitioned to CPB. Thromboelas- tography (TEG 6s; Citrated, Haemonetics Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA) performed prior to FFP transfusion showed markedly prolonged R time (38 minutes) (Figure 2). The rapid TEG channel of this test uses kaolin, tissue factor and calcium chloride as activators. Following FFP transfusion, the R time decreased substantially (10.1 minutes).
The CPB circuit consisted of a Capiox FX05 Baby-FX hollow fibre oxygenator (Terumo Corporation, Japan) and SMARxT coated tubing (LivaNova, VIC). The circuit was primed with 200 mL FFP, 280 mL packed red blood cells (to account for haemodilution related to FFP transfusion), 1400 IU heparin, 70 mL Plasma-Lyte 148 (Baxter, NSW), haemofiltered to achieve a haemato- crit of 28% and balanced with sodium bicarbonate and calcium chloride. The aortic cross clamp was applied for 13 minutes and total CPB time was 25 minutes. No fur- ther heparin was required during CPB and ACT (Hemochron Jr. Signature+, Werfen Australia, NSW) values remained within the desired range (Table 2).
As an added precaution, paired ACT were performed at every time point due to the known variability in results (Table 2). ACT was also measured using two car- tridge types; the low range (ACT-LR) cartridge (JACT-LR, Werfen Australia, NSW) comprised of a
dried preparation of celite, potato dextrin, stabilisers and buffers and is suitable for heparin concentrations up to 2.5 i.u./mL of blood and the high range (ACT-HR) cartridge (JACT+, Werfen Australia, NSW) which comprised of a dried preparation of silica, kaolin, phos- pholipid, stabilisers and buffers and is suitable for hepa- rin concentrations of 1 to 6i.u./mL of blood (Werfen Australia, NSW).
After weaning from CPB, modified ultrafiltration was completed and protamine reversal of heparin (60mg Protamine Sulphate (Salmon) injection 1%; Sanofi, AUS) returned the ACT to baseline. There was no unusual bleeding and haemostasis was straightforward. The R time was 10.7 minutes (reference range 4.5 to 9.1 min- utes; TEG® 6s; Citrated, Haemonetics Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA). There was no significant haemor- rhage in the post-operative period. FXII levels remained low when measured at 24- and 48-hours post FFP, and the child was discharged uneventfully on postoperative day four (Table 1).
Discussion
In our case, FXII deficiency was detected during routine pre-operativeworkup.Itinterfereswithtraditionalantico- agulation management strategies using ACT measurement
25 NOVEMBER 2021 | www.anzcp.org