Page 238 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 238
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
▪ As antidote in barbiturates poisoning.
▪ As analeptic.
c) Diterpenes
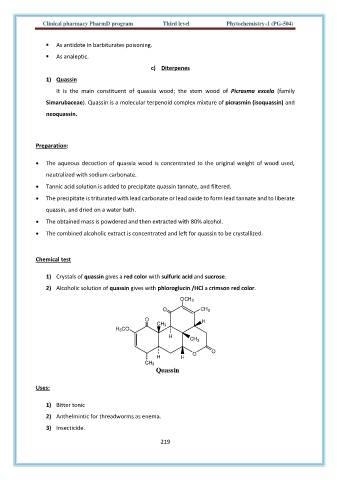
1) Quassin
It is the main constituent of quassia wood; the stem wood of Picrasma excela (family
Simarubaceae). Quassin is a molecular terpenoid complex mixture of picrasmin (isoquassin) and
neoquassin.
Preparation:
• The aqueous decoction of quassia wood is concentrated to the original weight of wood used,
neutralized with sodium carbonate.
• Tannic acid solution is added to precipitate quassin tannate, and filtered.
• The precipitate is triturated with lead carbonate or lead oxide to form lead tannate and to liberate
quassin, and dried on a water bath.
• The obtained mass is powdered and then extracted with 80% alcohol.
• The combined alcoholic extract is concentrated and left for quassin to be crystallized.
Chemical test
1) Crystals of quassin gives a red color with sulfuric acid and sucrose.
2) Alcoholic solution of quassin gives with phloroglucin /HCl a crimson red color.
OCH 3
O CH 3
O H
CH 3
H 3 CO
H CH 3
O
O
H H
CH 3
Quassin
Uses:
1) Bitter tonic
2) Anthelmintic for threadworms as enema.
3) Insecticide.
219