Page 149 - March 23 2022 Boinghams NYC Indian and Himalayan Art
P. 149
Indian Court Paintings
8
10
9
The second section of this sale (lots 466 through 499) offers a rich selection 479). Two paintings of Radha at her toilette (lots 470 and 473) as well as a later, 11
12 Pahari
of Indian court painting deserving of introduction. The Indian subcontinent yet exquisitely executed painting of a love-lorn Nayika (lot 474), showcase the
is vast, and most urban centers fostered a school of painting. These schools romantic tendencies of the artists of the Pahari courts. Schools
flourished from the 16th century through to the early 20th century under the
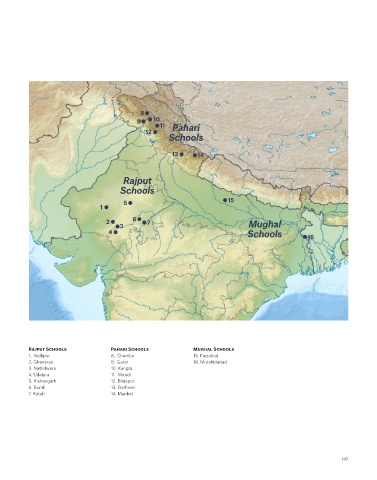
patronage of royal and princely patrons, recording the passions, pastimes, RAJPUT SCHOOLS: 13 14
religious texts and courtly pomp and circumstance. Indian painting can be Centered mainly in the famous towns of Jaipur, Jodhpur and Udaipur in
divided into distinct yet interrelated schools that underpin the diversity and Rajasthan, the Rajput schools arose as early as the 12th century from
creative genius of the subcontinent. The present sale offer’s paintings from indigenous schools of Western Indian painting, and typically depict palace
almost every corner of the subcontinent, from the duly celebrated workshops activity, hunting subjects and religious scenes, notably those of the life of
in Kangra to splendid courts like Ghanerao now faded into obscurity. Krishna. It was not until the 17th century, when many Mughal miniaturists Rajput
The selection showcases many folios from larger series on dynamic epics, worked at the ateliers of Rajput princely states, that distinct schools of
Schools
such as the Ramayana, the Bhagavata Purana, the Harivamsa, the Rukmini court panting began to arise; and while Rajput paintings are influenced by 15
Haran, the Gita Govinda, the Shiva Rahasya, and the Devi Mahatmya. Other Mughal art, the individual schools incorporate strong local elements with bold 5
1
paintings feature princely pleasures, genre scenes, nayikas, and ragamalas, the colors and strong profiles. There are countless schools of Rajput painting;
illustration of musical modes. The diversity of this group is highlighted not the selection here includes works from notable centers such as Jodhpur, 6
only by geography and subject, but also medium, highlighting two admirable Udaipur, Kotah, Bundi, and Kishangarh, and also includes resplendent works 2 7
3 Mughal
examples of picchwai paintings, a Jain yantra painting, as well as a rare from smaller schools such as that of the court of Ghanerao. A Mewari Gita
4
and large Mewar court painting on cloth. These paintings also come from Govinda produced for Maharana Sangram Singh in 1714 (lot 489) showcases Schools 16
some of the most storied collections of Indian painting, including the Royal the artistic styles of the relatively nascent periods of these court ateliers.
Mandi Library, the eminent civil servant Dr. Alma Latifi, the Garhwali activist Later works, such as the large format painting of Shiva sporting in the
and scholar Mukandi Lal, the famed Indian art dealer C.L. Bharany, the art sacred mountains, dated to 1827 (lot 495), demonstrate the evolution of the
historian W.G. Archer, British East India Company Officials Sir Elijah and Lady Rajput schools. Two wonderfully executed 19th century picchwai paintings
Mary Impey, the eclectic arts patron Paul F. Walter and the passionate Indian from Nathdwara (lots 498 and 499) highlight the diversity of the Rajasthani
miniature collector Dr. William Ehrenfeld. painting tradition.
PAHARI SCHOOLS: MUGHAL SCHOOLS
The Pahari region refers to the Himalayan foothills in the north of India, The Mughal dynasty, with its origins in Central Asia, was heavily influenced
encompassing the courts of Kangra, Guler, Mandi, Chamba, Mankot, Garhwal, by Persian cultural trends, which they took to new heights of artistic realism.
and Bilaspur, among many others. A great number of these local courts The Mughals were best known for their fusion of Indo-Islamic culture, and
developed a rich painting tradition, which flourished particularly in the 18th early emperors — particularly Akbar (1556-1605) — commissioned paintings
and 19th centuries. The Pahari style is very much rooted in the local landscape, to illustrate Hindu epics as well as various Persian texts. Akbar and his son
which is often used as a backdrop for Hindu epics like the Ramayana (lots Jahangir (r. 1605-1627) were also fascinated by European masters. In addition
466, 467, and 475), Gita Govinda, and Harivamsa (lot 471). These works can to Persian and Indo-Islamic influences, Mughal paintings show the impact of
be characterized by their soft clean lines and flowing pastel color schemes, as Renaissance techniques, such as chiaroscuro for shading and modeling, as
well as an unusually effective use of negative space and complex architectural well as Christian motifs, including cherubs.
compositions. This sale features works from some of the most admired artists In the twilight era of the Mughal empire, various cities in the Mughal provinces Rajput Schools Pahari Schools Mughal Schools
of the Kangra and Guler Pahari courts, including two folios from a Ramayana established their own schools of painting centered on cities such as Lucknow, 1. Jodhpur 8. Chamba 15. Faizabad
painted by the first Generation after Manaku and Nainsukh (lots 466 and Faizabad and Murshidabad, which later became known as the ‘Provincial 2. Ghanerao 9. Guler 16. Murshidabad
467), as well as works that can be attributed to the later Kangra Court artists Mughal’ style. This sale includes a work by one of the most celebrated Awadhi 3. Nathdwara 10. Kangra
Purkhu (lot 471). The Pahari section also includes a dynamic folio from a masters Mihr Chand (active c. 1759-86), who is acknowledged for instituting 4. Udaipur 11. Mandi
Rukmini Haran series by the trailblazing Garhwali artist Mola Ram (lot 478) an imperialist revival style in late 18th century Faizabad. His painting, “Woman 5. Kishangarh 12. Bilaspur
and a noble portrait in the style of Meju, the Master of the Mankot court (lot at the Well,” (lot 483) inspired by a classical Mughal subject and Shah Jahan 6. Bundi 13. Garhwal
era motifs, is a hallmark of the Mihr Chand’s Faizabad workshop. 7. Kotah 14. Mankot
146 147