Page 33 - Building Digital Libraries
P. 33
CHAPTER 2
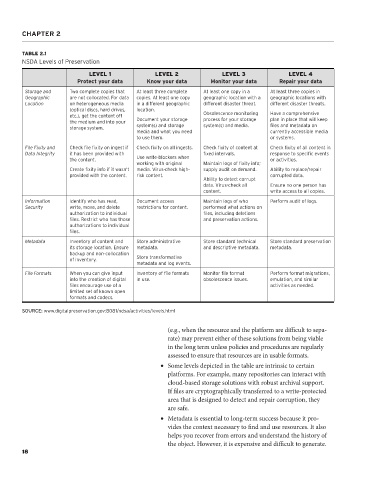
TABLE 2.1
NSDA Levels of Preservation
LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3 LEVEL 4
Protect your data Know your data Monitor your data Repair your data
Storage and Two complete copies that At least three complete At least one copy in a At least three copies in
Geographic are not collocated. For data copies. At least one copy geographic location with a geographic locations with
Location on heterogeneous media in a different geographic different disaster threat. different disaster threats.
(optical discs, hard drives, location.
etc.), get the content off Obsolescence monitoring Have a comprehensive
the medium and into your Document your storage process for your storage plan in place that will keep
storage system. system(s) and storage system(s) and media. files and metadata on
media and what you need currently accessible media
to use them. or systems.
File Fixity and Check file fixity on ingest if Check fixity on all ingests. Check fixity of content at Check fixity of all content in
Data Integrity it has been provided with fixed intervals. response to specific events
the content. Use write-blockers when or activities.
working with original Maintain logs of fixity info;
Create fixity info if it wasn’t media. Virus-check high- supply audit on demand. Ability to replace/repair
provided with the content. risk content. corrupted data.
Ability to detect corrupt
data. Virus-check all Ensure no one person has
content. write access to all copies.
Information Identify who has read, Document access Maintain logs of who Perform audit of logs.
Security write, move, and delete restrictions for content. performed what actions on
authorization to individual files, including deletions
files. Restrict who has those and preservation actions.
authorizations to individual
files.
Metadata Inventory of content and Store administrative Store standard technical Store standard preservation
its storage location. Ensure metadata. and descriptive metadata. metadata.
backup and non-collocation
of inventory. Store transformative
metadata and log events.
File Formats When you can give input Inventory of file formats Monitor file format Perform format migrations,
into the creation of digital in use. obsolescence issues. emulation, and similar
files encourage use of a activities as needed.
limited set of known open
formats and codecs.
SOURCE: www.digitalpreservation.gov:8081/ndsa/activities/levels.html
(e.g., when the resource and the platform are difficult to sepa-
rate) may prevent either of these solutions from being viable
in the long term unless policies and procedures are regularly
assessed to ensure that resources are in usable formats.
• Some levels depicted in the table are intrinsic to certain
platforms. For example, many repositories can interact with
cloud-based storage solutions with robust archival support.
If files are cryptographically transferred to a write-protected
area that is designed to detect and repair corruption, they
are safe.
• Metadata is essential to long-term success because it pro-
vides the context necessary to find and use resources. It also
helps you recover from errors and understand the history of
the object. However, it is expensive and difficult to generate.
18