Page 29 - MSC & Exosomes in autoimmune
P. 29
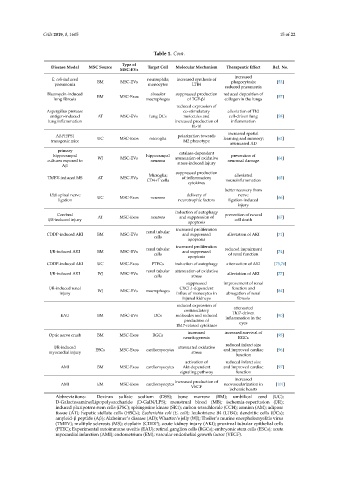
Cells 2019, 8, 1605 15 of 22
Table 1. Cont.
Type of
Disease Model MSC Source Target Cell Molecular Mechanism Therapeutic Effect Ref. No.
MSC-EVs
increased
E. coli-induced neutrophils; increased synthesis of
BM MSC-EVs phagocytosis; [53]
pneumonia monocytes LTB4
reduced pneumonia
Bleomycin-induced alveolar suppressed production reduced deposition of
lung fibrosis BM MSC-Exos macrophages of TGF-β1 collagen in the lungs [57]
reduced expression of
Aspergillus protease co-stimulatory alleviation of Th2
antigen-induced AT MSC-EVs lung DCs molecules and cell-driven lung [58]
lung inflammation increased production of inflammation
IL-10
increased spatial
AβPP/PS1 polarization towards
transgenic mice UC MSC-Exos microglia M2 phenotype learning and memory; [62]
attenuated AD
primary
catalase-dependent
hippocampal hippocampal prevention of
cultures exposed to WJ MSC-EVs neurons attenuation of oxidative neuronal damage [64]
stress-induced injury
Aβ
suppressed production
Microglia; alleviated
TMEV-induced MS AT MSC-EVs of inflammatory [65]
CD4+T cells neuroinflammation
cytokines
better recovery from
L5/6 spinal nerve delivery of nerve
ligation UC MSC-Exos neurons neurotrophic factors ligation-induced [66]
injury
induction of autophagy
Cerebral AT MSC-Exos neurons and suppression of prevention of neural [67]
I/R-induced injury cell death
apoptosis
increased proliferation
renal tubular
CDDP-induced AKI BM MSC-EVs and suppressed alleviation of AKI [71]
cells
apoptosis
increased proliferation
renal tubular reduced impairment
I/R-induced AKI BM MSC-EVs and suppressed [74]
cells of renal function
apoptosis
CDDP-induced AKI UC MSC-Exos PTECs induction of autophagy attenuation of AKI [75,76]
renal tubular attenuation of oxidative
I/R-induced AKI WJ MSC-EVs alleviation of AKI [77]
cells stress
suppressed improvement of renal
I/R-induced renal WJ MSC-EVs macrophages CXCL1-dependent function and [84]
injury influx of monocytes in abrogation of renal
injured kidneys fibrosis
reduced expression of
attenuated
costimulatory
EAU BM MSC-EVs DCs molecules and reduced Th17-driven [90]
inflammation in the
production of
Th17-related cytokines eyes
increased increased survival of
Optic nerve crush BM MSC-Exos RGCs [95]
neuritogenesis RGCs
reduced infarct size
I/R-induced attenuated oxidative
ESCs MSC-Exos cardiomyocytes and improved cardiac [96]
myocardial injury stress
function
activation of reduced infarct size
AMI BM MSC-Exos cardiomyocytes Akt-dependent and improved cardiac [97]
signaling pathway function
increased
increased production of
AMI EM MSC-Exos cardiomyocytes neovascularization in [101]
VEGF
ischemic hearts
Abbreviations: Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS); bone marrow (BM); umbilical cord (UC);
D-Galactosamine/Lipopolysaccharide (D-GalN/LPS); menstrual blood (MB); ischemia-reperfusion (I/R);
induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC); sphingosine kinase (SK1); carbon tetrachloride (CCl4); amnion (AM); adipose
tissue (AT); hepatic stellate cells (HSCs); Escherichia coli (E. coli); leukotriene B4 (LTB4); dendritic cells (DCs);
amyloid-β peptide (Aβ); Alzheimer’s disease (AD); Wharton’s jelly (WJ); Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus
(TMEV); multiple sclerosis (MS); cisplatin (CDDP); acute kidney injury (AKI); proximal tubular epithelial cells
(PTEC); Experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU); retinal ganglion cells (RGCs); embryonic stem cells (ESCs); acute
myocardial infarction (AMI); endometrium (EM); vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).