Page 31 - JOP2020_FINAL2.pf
P. 31
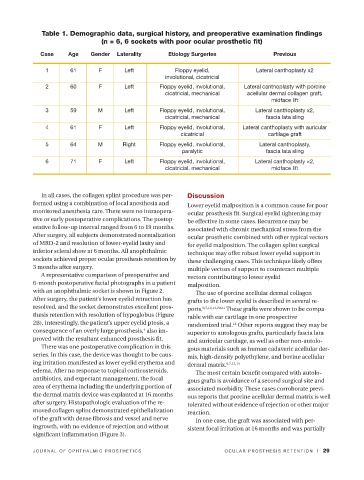
Table 1. Demographic data, surgical history, and preoperative examination findings
(n = 6, 6 sockets with poor ocular prosthetic fit)
Case Age Gender Laterality Etiology Surgeries Previous
1 61 F Left Floppy eyelid, Lateral canthoplasty x2
involutional, cicatricial
2 60 F Left Floppy eyelid, involutional, Lateral canthoplasty with porcine
12B
cicatricial, mechanical acellular dermal collagen graft,
midface lift
3 59 M Left Floppy eyelid, involutional, Lateral canthoplasty x2,
cicatricial, mechanical fascia lata sling
4 61 F Left Floppy eyelid, involutional, Lateral canthoplasty with auricular
cicatricial cartilage graft
5 64 M Right Floppy eyelid, involutional, Lateral canthoplasty,
paralytic fascia lata sling
6 71 F Left Floppy eyelid, involutional, Lateral canthoplasty ×2,
cicatricial, mechanical midface lift
In all cases, the collagen splint procedure was per- Discussion
formed using a combination of local anesthesia and Lower eyelid malposition is a common cause for poor
monitored anesthesia care. There were no intraopera- ocular prosthesis fit. Surgical eyelid tightening may
tive or early postoperative complications. The postop- be effective in some cases. Recurrence may be
erative follow-up interval ranged from 6 to 19 months. associated with chronic mechanical stress from the
After surgery, all subjects demonstrated normalization ocular prosthetic combined with other typical vectors
of MRD-2 and resolution of lower-eyelid laxity and for eyelid malposition. The collagen splint surgical
inferior scleral show at 6 months. All anophthalmic technique may offer robust lower eyelid support in
sockets achieved proper ocular prosthesis retention by these challenging cases. This technique likely offers
3 months after surgery. multiple vectors of support to counteract multiple
A representative comparison of preoperative and vectors contributing to lower eyelid
6-month postoperative facial photographs in a patient malposition.
with an anophthalmic socket is shown in Figure 2. The use of porcine acellular dermal collagen
After surgery, the patient’s lower eyelid retraction has grafts to the lower eyelid is described in several re-
resolved, and the socket demonstrates excellent pros- ports. 6,7,13,14,20,21 These grafts were shown to be compa-
thesis retention with resolution of hypoglobus (Figure rable with ear cartilage in one prospective
2B). Interestingly, the patient’s upper eyelid ptosis, a randomized trial. Other reports suggest they may be
14
4
consequence of an overly large prosthesis, also im- superior to autologous grafts, particularly fascia lata
proved with the resultant enhanced prosthesis fit. and auricular cartilage, as well as other non-autolo-
There was one postoperative complication in this gous materials such as human cadaveric acellular der-
series. In this case, the device was thought to be caus- mis, high-density polyethylene, and bovine acellular
ing irritation manifested as lower eyelid erythema and dermal matrix. 6,7,13,14
edema. After no response to topical corticosteroids, The most certain benefit compared with autolo-
antibiotics, and expectant management, the focal gous grafts is avoidance of a second surgical site and
area of erythema including the underlying portion of associated morbidity. These cases corroborate previ-
the dermal matrix device was explanted at 16 months ous reports that porcine acellular dermal matrix is well
after surgery. Histopathologic evaluation of the re- tolerated without evidence of rejection or other major
moved collagen splint demonstrated epithelialization reaction.
of the graft with dense fibrosis and vessel and nerve In one case, the graft was associated with per-
ingrowth, with no evidence of rejection and without sistent focal irritation at 16 months and was partially
significant inflammation (Figure 3).
JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMIC PROSTHETICS OCULAR PROSTHESIS RETENTION | 29