Page 45 - Biblical Counseling II-Textbook
P. 45
hands. The cerebellum also helps process and store memories for things we cannot consciously recall,
such as why we link the sound of thunder to a flash of lightning (Myers, 2009). (photo from:
www.blogmicroscopeworld.com)
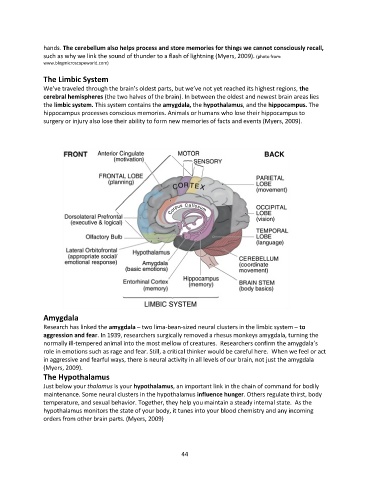
The Limbic System
We’ve traveled through the brain’s oldest parts, but we’ve not yet reached its highest regions, the
cerebral hemispheres (the two halves of the brain). In between the oldest and newest brain areas lies
the limbic system. This system contains the amygdala, the hypothalamus, and the hippocampus. The
hippocampus processes conscious memories. Animals or humans who lose their hippocampus to
surgery or injury also lose their ability to form new memories of facts and events (Myers, 2009).
Amygdala
Research has linked the amygdala – two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system – to
aggression and fear. In 1939, researchers surgically removed a rhesus monkeys amygdala, turning the
normally ill-tempered animal into the most mellow of creatures. Researchers confirm the amygdala’s
role in emotions such as rage and fear. Still, a critical thinker would be careful here. When we feel or act
in aggressive and fearful ways, there is neural activity in all levels of our brain, not just the amygdala
(Myers, 2009).
The Hypothalamus
Just below your thalamus is your hypothalamus, an important link in the chain of command for bodily
maintenance. Some neural clusters in the hypothalamus influence hunger. Others regulate thirst, body
temperature, and sexual behavior. Together, they help you maintain a steady internal state. As the
hypothalamus monitors the state of your body, it tunes into your blood chemistry and any incoming
orders from other brain parts. (Myers, 2009)
44