Page 41 - Seasonal Produce Guide
P. 41
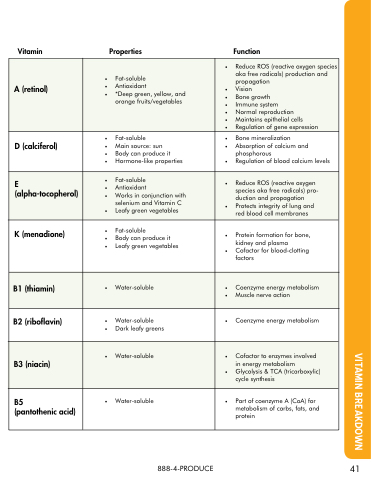
Vitamin Properties
Function
A (retinol)
• • Fat-soluble
• • • Antioxidant
• • *Deep green yellow and
orange fruits/vegetables
• Reduce ROS (reactive oxygen species aka free radicals) production and
propagation
• • Vision
• • • Bone growth
• • • Immune system
• • • Normal reproduction
• • • Maintains epithelial cells
• • Regulation of gene expression
D (calciferol)
• • Fat-soluble
• • • Main source: sun
• • • Body can produce it • • Hormone-like properties
• • Bone mineralization
• • Absorption of calcium and
phosphorous
• Regulation of blood calcium levels
E (alpha-tocopherol)
• • Fat-soluble
• • • Antioxidant
• • Works in in conjunction with
selenium and
Vitamin C
• Leafy green vegetables
• Reduce ROS (reactive oxygen species aka free radicals) pro- duction and
propagation
• Protects integrity of lung and
and
red blood cell membranes
K (menadione)
• • Fat-soluble
• • • Body can produce it • • Leafy green vegetables
• Protein formation for for bone kidney and
plasma
• Cofactor for blood-clotting factors
B1 (thiamin)
• Water-soluble
• • Coenzyme energy metabolism
• • Muscle nerve action
B2 (riboflavin)
• • Water-soluble
• • Dark leafy greens
• Coenzyme energy metabolism
B3 (niacin)
• Water-soluble
• Cofactor to to enzymes involved in energy metabolism
• Glycolysis & TCA (tricarboxylic) cycle synthesis
B5
(pantothenic acid)
• Water-soluble
• Part of of coenzyme A A (CoA) for metabolism
of carbs fats and
protein
888-4-PRODUCE
41
VITAMIN BREAKDOWN