Page 45 - CASA Bulletin of Anesthesiology 2022; 9(2) (5)
P. 45
Vol. 9, No 2, 2022
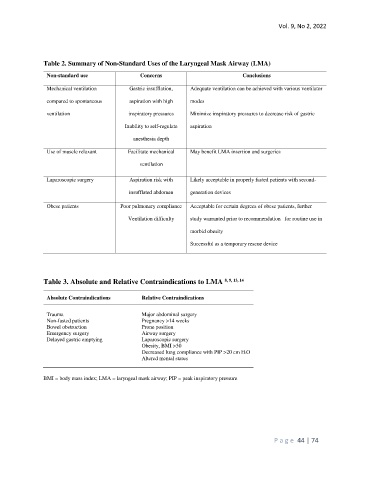
Table 2. Summary of Non-Standard Uses of the Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)
Non-standard use Concerns Conclusions
Mechanical ventilation Gastric insufflation, Adequate ventilation can be achieved with various ventilator
compared to spontaneous aspiration with high modes
ventilation inspiratory pressures Minimize inspiratory pressures to decrease risk of gastric
Inability to self-regulate aspiration
anesthesia depth
Use of muscle relaxant Facilitate mechanical May benefit LMA insertion and surgeries
ventilation
Laparoscopic surgery Aspiration risk with Likely acceptable in properly fasted patients with second-
insufflated abdomen generation devices
Obese patients Poor pulmonary compliance Acceptable for certain degrees of obese patients, further
Ventilation difficulty study warranted prior to recommendation for routine use in
morbid obesity
Successful as a temporary rescue device
Table 3. Absolute and Relative Contraindications to LMA 8, 9, 13, 14
Absolute Contraindications Relative Contraindications
Trauma Major abdominal surgery
Non-fasted patients Pregnancy >14 weeks
Bowel obstruction Prone position
Emergency surgery Airway surgery
Delayed gastric emptying Laparoscopic surgery
Obesity, BMI >30
Decreased lung compliance with PIP >20 cm H 2O
Altered mental status
BMI = body mass index; LMA = laryngeal mask airway; PIP = peak inspiratory pressure
P a g e 44 | 74