Page 494 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 494
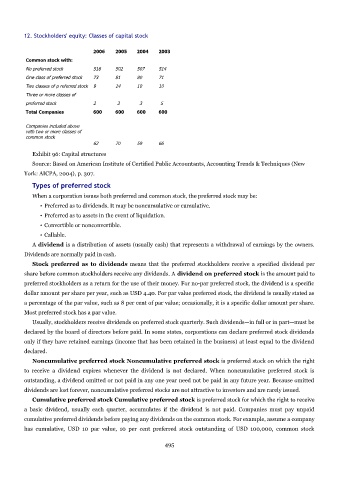
12. Stockholders' equity: Classes of capital stock
2006 2005 2004 2003
Common stock with:
No preferred stock 516 502 507 514
One class of preferred stock 73 81 80 71
Two classes of p referred stock 9 14 10 10
Three or more classes of
preferred stock 2 3 3 5
Total Companies 600 600 600 600
Companies included above
with two or more classes of
common stock
62 70 59 66
Exhibit 96: Capital structures
Source: Based on American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, Accounting Trends & Techniques (New
York: AICPA, 2004), p. 307.
Types of preferred stock
When a corporation issues both preferred and common stock, the preferred stock may be:
• Preferred as to dividends. It may be noncumulative or cumulative.
• Preferred as to assets in the event of liquidation.
• Convertible or nonconvertible.
• Callable.
A dividend is a distribution of assets (usually cash) that represents a withdrawal of earnings by the owners.
Dividends are normally paid in cash.
Stock preferred as to dividends means that the preferred stockholders receive a specified dividend per
share before common stockholders receive any dividends. A dividend on preferred stock is the amount paid to
preferred stockholders as a return for the use of their money. For no-par preferred stock, the dividend is a specific
dollar amount per share per year, such as USD 4.40. For par value preferred stock, the dividend is usually stated as
a percentage of the par value, such as 8 per cent of par value; occasionally, it is a specific dollar amount per share.
Most preferred stock has a par value.
Usually, stockholders receive dividends on preferred stock quarterly. Such dividends—in full or in part—must be
declared by the board of directors before paid. In some states, corporations can declare preferred stock dividends
only if they have retained earnings (income that has been retained in the business) at least equal to the dividend
declared.
Noncumulative preferred stock Noncumulative preferred stock is preferred stock on which the right
to receive a dividend expires whenever the dividend is not declared. When noncumulative preferred stock is
outstanding, a dividend omitted or not paid in any one year need not be paid in any future year. Because omitted
dividends are lost forever, noncumulative preferred stocks are not attractive to investors and are rarely issued.
Cumulative preferred stock Cumulative preferred stock is preferred stock for which the right to receive
a basic dividend, usually each quarter, accumulates if the dividend is not paid. Companies must pay unpaid
cumulative preferred dividends before paying any dividends on the common stock. For example, assume a company
has cumulative, USD 10 par value, 10 per cent preferred stock outstanding of USD 100,000, common stock
495