Page 81 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 81
2. Recording business transactions
A liability, accounts payable, decreases (debited); and an asset, cash, decreases (credited) by USD 1,400.
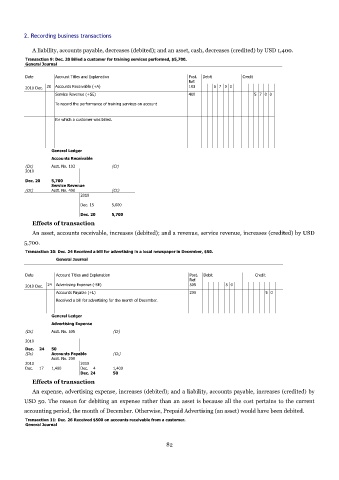
Transaction 9: Dec. 20 Billed a customer for training services performed, $5,700.
General Journal
Date Account Titles and Explanation Post. Debit Credit
Ref.
2010 Dec. 20 Accounts Receivable (+A) 103 5 7 0 0
Service Revenue (+SE) 400 5 7 0 0
To record the performance of training services on account
for which a customer was billed.
General Ledger
Accounts Receivable
(Dr.) Acct. No. 103 (Cr)
2010
Dec. 20 5,700
Service Revenue
(Dr.) Acct. No. 400 (Cr.)
2010
Dec. 15 5,000
Dec. 20 5,700
Effects of transaction
An asset, accounts receivable, increases (debited); and a revenue, service revenue, increases (credited) by USD
5,700.
Transaction 10: Dec. 24 Received a bill for advertising in a local newspaper in December, $50.
General Journal
Date Account Titles and Explanation Post. Debit Credit
Ref.
2010 Dec. 24 Advertising Expense (-SE) 505 5 0
Accounts Payable (+L) 200 5 0
Received a bill for advertising for the month of December.
General Ledger
Advertising Expense
(Dr.) Acct. No. 505 (Cr)
2010
Dec. 24 50
(Dr.) Accounts Payable (Cr.)
Acct. No. 200
2010 2010
Dec. 17 1,400 Dec. 4 1,400
Dec. 24 50
Effects of transaction
An expense, advertising expense, increases (debited); and a liability, accounts payable, increases (credited) by
USD 50. The reason for debiting an expense rather than an asset is because all the cost pertains to the current
accounting period, the month of December. Otherwise, Prepaid Advertising (an asset) would have been debited.
Transaction 11: Dec. 26 Received $500 on accounts receivable from a customer.
General Journal
82