Page 115 - PowerPoint 演示文稿
P. 115
Bifocal Lenses 105
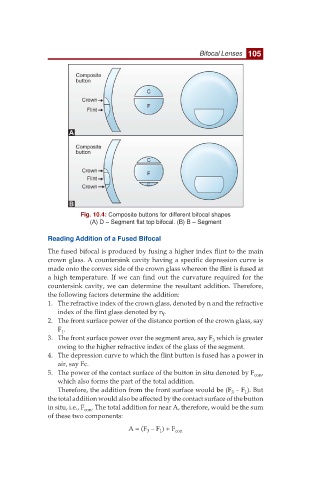
Fig. 10.4: Composite buttons for different bifocal shapes
(A) D – Segment flat top bifocal. (B) B – Segment
Reading Addition of a Fused Bifocal
The fused bifocal is produced by fusing a higher index flint to the main
crown glass. A countersink cavity having a specific depression curve is
made onto the convex side of the crown glass whereon the flint is fused at
a high temperature. If we can find out the curvature required for the
countersink cavity, we can determine the resultant addition. Therefore,
the following factors determine the addition:
1. The refractive index of the crown glass, denoted by n and the refractive
index of the flint glass denoted by n .
f
2. The front surface power of the distance portion of the crown glass, say
F .
1
3. The front surface power over the segment area, say F which is greater
3
owing to the higher refractive index of the glass of the segment.
4. The depression curve to which the flint button is fused has a power in
air, say Fc.
5. The power of the contact surface of the button in situ denoted by F con ,
which also forms the part of the total addition.
Therefore, the addition from the front surface would be (F – F ). But
3
1
the total addition would also be affected by the contact surface of the button
in situ, i.e., F con . The total addition for near A, therefore, would be the sum
of these two components:
A = (F – F ) + F con
3
1