Page 108 - Keys to College Success
P. 108
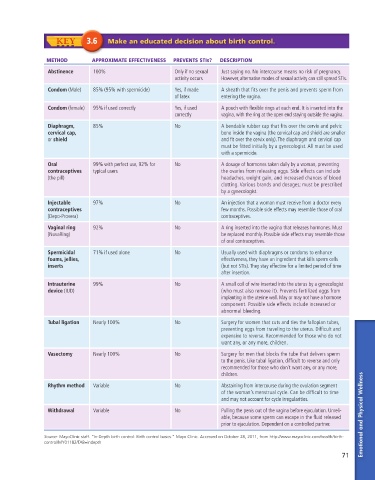
KEY 3.6 Make an educated decision about birth control.
METHOD APPROXIMATE EFFECTIVENESS PREVENTS STIs? DESCRIPTION
Abstinence 100% Only if no sexual Just saying no. No intercourse means no risk of pregnancy.
activity occurs However, alternative modes of sexual activity can still spread STIs.
Condom (Male) 85% (95% with spermicide) Yes, if made A sheath that fits over the penis and prevents sperm from
of latex entering the vagina.
Condom (female) 95% if used correctly Yes, if used A pouch with flexible rings at each end. It is inserted into the
correctly vagina, with the ring at the open end staying outside the vagina.
Diaphragm, 85% No A bendable rubber cap that fits over the cervix and pelvic
cervical cap, bone inside the vagina (the cervical cap and shield are smaller
or shield and fit over the cervix only). The diaphragm and cervical cap
must be fitted initially by a gynecologist. All must be used
with a spermicide.
Oral 99% with perfect use, 92% for No A dosage of hormones taken daily by a woman, preventing
contraceptives typical users the ovaries from releasing eggs. Side effects can include
(the pill) headaches, weight gain, and increased chances of blood
clotting. Various brands and dosages; must be prescribed
by a gynecologist.
Injectable 97% No An injection that a woman must receive from a doctor every
contraceptives few months. Possible side effects may resemble those of oral
(Depo-Provera) contraceptives.
Vaginal ring 92% No A ring inserted into the vagina that releases hormones. Must
(NuvaRing) be replaced monthly. Possible side effects may resemble those
of oral contraceptives.
Spermicidal 71% if used alone No Usually used with diaphragms or condoms to enhance
foams, jellies, effectiveness, they have an ingredient that kills sperm cells
inserts (but not STIs). They stay effective for a limited period of time
after insertion.
Intrauterine 99% No A small coil of wire inserted into the uterus by a gynecologist
device (IUD) (who must also remove it). Prevents fertilized eggs from
implanting in the uterine wall. May or may not have a hormone
component. Possible side effects include increased or
abnormal bleeding.
Tubal ligation Nearly 100% No Surgery for women that cuts and ties the fallopian tubes,
preventing eggs from traveling to the uterus. Difficult and
expensive to reverse. Recommended for those who do not
want any, or any more, children.
Vasectomy Nearly 100% No Surgery for men that blocks the tube that delivers sperm
to the penis. Like tubal ligation, difficult to reverse and only
recommended for those who don’t want any, or any more,
children.
Rhythm method Variable No Abstaining from intercourse during the ovulation segment
of the woman’s menstrual cycle. Can be difficult to time
and may not account for cycle irregularities.
Withdrawal Variable No Pulling the penis out of the vagina before ejaculation. Unreli-
able, because some sperm can escape in the fluid released Emotional and Physical Wellness
prior to ejaculation. Dependent on a controlled partner.
Source: MayoClinic staff. “In-Depth birth control: Birth control basics.” Mayo Clinic. Accessed on October 28, 2011, from http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/birth-
control/MY01182/TAB=indepth
71