Page 288 - Keys To Community College Success
P. 288
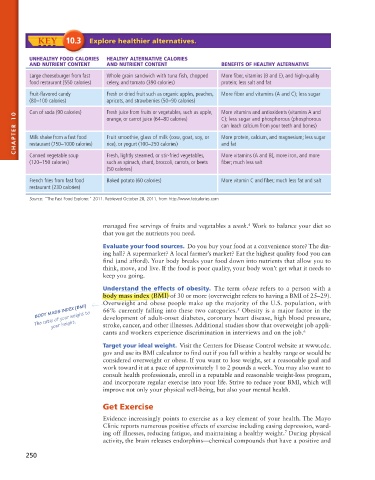
KEY 10.3 Explore healthier alternatives.
UNHEALTHY FOOD CALORIES HEALTHY ALTERNATIVE CALORIES
AND NUTRIENT CONTENT AND NUTRIENT CONTENT BENEFITS OF HEALTHY ALTERNATIVE
Large cheeseburger from fast Whole grain sandwich with tuna fish, chopped More fiber, vitamins (B and E), and high-quality
food restaurant (550 calories) celery, and tomato (390 calories) protein; less salt and fat
Fruit-flavored candy Fresh or dried fruit such as organic apples, peaches, More fiber and vitamins (A and C); less sugar
(80–100 calories) apricots, and strawberries (50–90 calories)
Can of soda (90 calories) Fresh juice from fruits or vegetables, such as apple, More vitamins and antioxidents (vitamins A and
10 orange, or carrot juice (64–80 calories) C); less sugar and phosphorous (phosphorous
CHAPTER Milk shake from a fast food Fruit smoothie, glass of milk (cow, goat, soy, or More protein, calcium, and magnesium; less sugar
can leach calcium from your teeth and bones)
restaurant (750–1000 calories)
and fat
rice), or yogurt (100–250 calories)
Canned vegetable soup
fiber; much less salt
(120–150 calories) Fresh, lightly steamed, or stir-fried vegetables, More vitamins (A and B), more iron, and more
such as spinach, chard, broccoli, carrots, or beets
(50 calories)
French fries from fast food Baked potato (60 calories) More vitamin C and fiber; much less fat and salt
restaurant (230 calories)
Source: “The Fast Food Explorer.” 2011. Retrieved October 28, 2011, from http://www.fatcalories.com
managed five servings of fruits and vegetables a week. Work to balance your diet so
4
that you get the nutrients you need.
Evaluate your food sources. Do you buy your food at a convenience store? The din-
ing hall? A supermarket? A local farmer’s market? Eat the highest quality food you can
find (and afford). Your body breaks your food down into nutrients that allow you to
think, move, and live. If the food is poor quality, your body won’t get what it needs to
keep you going.
Understand the effects of obesity. The term obese refers to a person with a
body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more (overweight refers to having a BMI of 25–29).
Overweight and obese people make up the majority of the U.S. population, with
BODY MASS INDEX (BMI)
5
The ratio of your weight to 66% currently falling into these two categories. Obesity is a major factor in the
development of adult-onset diabetes, coronary heart disease, high blood pressure,
your height.
stroke, cancer, and other illnesses. Additional studies show that overweight job appli-
cants and workers experience discrimination in interviews and on the job. 6
Target your ideal weight. Visit the Centers for Disease Control website at www.cdc.
gov and use its BMI calculator to find out if you fall within a healthy range or would be
considered overweight or obese. If you want to lose weight, set a reasonable goal and
work toward it at a pace of approximately 1 to 2 pounds a week. You may also want to
consult health professionals, enroll in a reputable and reasonable weight-loss program,
and incorporate regular exercise into your life. Strive to reduce your BMI, which will
improve not only your physical well-being, but also your mental health.
Get Exercise
Evidence increasingly points to exercise as a key element of your health. The Mayo
Clinic reports numerous positive effects of exercise including easing depression, ward-
ing off illnesses, reducing fatigue, and maintaining a healthy weight. During physical
7
activity, the brain releases endorphins—chemical compounds that have a positive and
250