Page 98 - Keys to College Success
P. 98
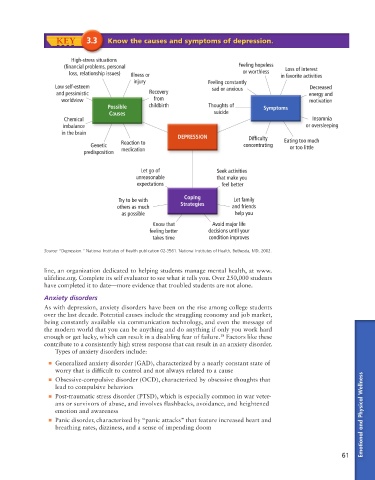
KEY 3.3 Know the causes and symptoms of depression.
High-stress situations
(financial problems, personal Feeling hopeless Loss of interest
loss, relationship issues) Illness or or worthless in favorite activities
injury Feeling constantly
Low self-esteem sad or anxious Decreased
and pessimistic Recovery energy and
worldview from motivation
Possible childbirth Thoughts of Symptoms
Causes suicide
Chemical Insomnia
imbalance or oversleeping
in the brain
DEPRESSION Difficulty
Reaction to Eating too much
Genetic concentrating or too little
predisposition medication
Let go of Seek activities
unreasonable that make you
expectations f feel better
Coping
Try to be with Let family
others as much Strategies and friends
as possible help you
Know that Avoid major life
feeling better decisions until your
takes time condition improves
Source: “Depression.” National Institutes of Health publication 02-3561. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, 2002.
line, an organization dedicated to helping students manage mental health, at www.
ulifeline.org. Complete its self evaluator to see what it tells you. Over 250,000 students
have completed it to date—more evidence that troubled students are not alone.
Anxiety disorders
As with depression, anxiety disorders have been on the rise among college students
over the last decade. Potential causes include the struggling economy and job market,
being constantly available via communication technology, and even the message of
the modern world that you can be anything and do anything if only you work hard
enough or get lucky, which can result in a disabling fear of failure. Factors like these
18
contribute to a consistently high stress response that can result in an anxiety disorder.
Types of anxiety disorders include:
■ Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), characterized by a nearly constant state of
worry that is difficult to control and not always related to a cause
■ Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), characterized by obsessive thoughts that
lead to compulsive behaviors
■ Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), which is especially common in war veter-
ans or survivors of abuse, and involves flashbacks, avoidance, and heightened
emotion and awareness
■ Panic disorder, characterized by “panic attacks” that feature increased heart and Emotional and Physical Wellness
breathing rates, dizziness, and a sense of impending doom
61