Page 3 - genveon oznur
P. 3
80 L. Elmer et al. / Journal of the Neurological Sciences 248 (2006) 78–83
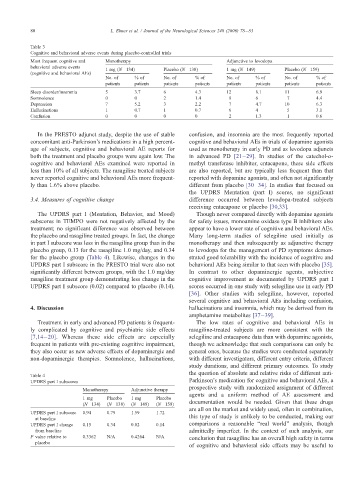
Table 3
Cognitive and behavioral adverse events during placebo-controlled trials
Most frequent cognitive and Monotherapy Adjunctive to levodopa
behavioral adverse events
1mg(N =134) Placebo (N =138) 1 mg (N =149) Placebo (N =159)
(cognitive and behavioral AEs)
No. of %of No. of %of No. of %of No. of %of
patients patients patients patients patients patients patients patients
Sleep disorder/insomnia 5 3.7 6 4.3 12 8.1 11 6.9
Somnolence 0 0 2 1.4 9 6 7 4.4
Depression 7 5.2 3 2.2 7 4.7 10 6.3
Hallucinations 1 0.7 1 0.7 6 4 5 3.1
Confusion 0 0 0 0 2 1.3 1 0.6
In the PRESTO adjunct study, despite the use of stable confusion, and insomnia are the most frequently reported
concomitant anti-Parkinson’s medications in a high percent- cognitive and behavioral AEs in trials of dopamine agonists
age of subjects, cognitive and behavioral AE reports for used as monotherapy in early PD and as levodopa adjuncts
both the treatment and placebo groups were again low. The in advanced PD [21–29]. In studies of the catechol-o-
cognitive and behavioral AEs examined were reported in methyl transferase inhibitor, entacapone, these side effects
less than 10% of all subjects. The rasagiline treated subjects are also reported, but are typically less frequent than that
never reported cognitive and behavioral AEs more frequent- reported with dopamine agonists, and often not significantly
ly than 1.6% above placebo. different from placebo [30–34]. In studies that focused on
the UPDRS Mentation (part I) scores, no significant
3.4. Measures of cognitive change difference occurred between levodopa-treated subjects
receiving entacapone or placebo [30,33].
The UPDRS part I (Mentation, Behavior, and Mood) Though never compared directly with dopamine agonists
subscores in TEMPO were not negatively affected by the for safety issues, monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors also
treatment; no significant difference was observed between appear to have a lower rate of cognitive and behavioral AEs.
the placebo and rasagiline treated groups. In fact, the change Many long-term studies of selegiline used initially as
in part I subscore was less in the rasagiline group than in the monotherapy and then subsequently as adjunctive therapy
placebo group, 0.13 for the rasagiline 1.0 mg/day, and 0.34 to levodopa for the management of PD symptoms demon-
for the placebo group (Table 4). Likewise, changes in the strated good tolerability with the incidence of cognitive and
UPDRS part I subscore in the PRESTO trial were also not behavioral AEs being similar to that seen with placebo [35].
significantly different between groups, with the 1.0 mg/day In contrast to other dopaminergic agents, subjective
rasagiline treatment group demonstrating less change in the cognitive improvement as documented by UPDRS part I
UPDRS part I subscore (0.02) compared to placebo (0.14). scores occurred in one study with selegiline use in early PD
[36]. Other studies with selegiline, however, reported
several cognitive and behavioral AEs including confusion,
4. Discussion hallucinations and insomnia, which may be derived from its
amphetamine metabolites [37–39].
Treatment in early and advanced PD patients is frequent- The low rates of cognitive and behavioral AEs in
ly complicated by cognitive and psychiatric side effects rasagiline-treated subjects are more consistent with the
[7,14–20]. Whereas these side effects are especially selegiline and entacapone data than with dopamine agonists,
frequent in patients with pre-existing cognitive impairment, though we acknowledge that such comparisons can only be
they also occur as new adverse effects of dopaminergic and general ones, because the studies were conducted separately
non-dopaminergic therapies. Somnolence, hallucinations, with different investigators, different entry criteria, different
study durations, and different primary outcomes. To study
the question of absolute and relative risks of different anti-
Table 4
UPDRS part I subscores Parkinson’s medication for cognitive and behavioral AEs, a
prospective study with randomized assignment of different
Monotherapy Adjunctive therapy
agents and a uniform method of AE assessment and
1mg Placebo 1mg Placebo
(N =134) (N =138) (N =149) (N =159) documentation would be needed. Given that these drugs
are all on the market and widely used, often in combination,
UPDRS part I subscore 0.94 0.79 1.59 1.72
at baseline this type of study is unlikely to be conducted, making our
UPDRS part I change 0.15 0.34 0.02 0.14 comparisons a reasonable ‘‘real world’’ analysis, though
from baseline admittedly imperfect. In the context of such analysis, our
P value relative to 0.3362 N/A 0.4264 N/A conclusion that rasagiline has an overall high safety in terms
placebo
of cognitive and behavioral side effects may be useful to