Page 62 - Global Maintenance Standard - NE_VOct 2020
P. 62
list. As a minimum, the list must include defects that could potentially occur on those parts listed in
appendix A of GMS 4. Safety Critical Parts.
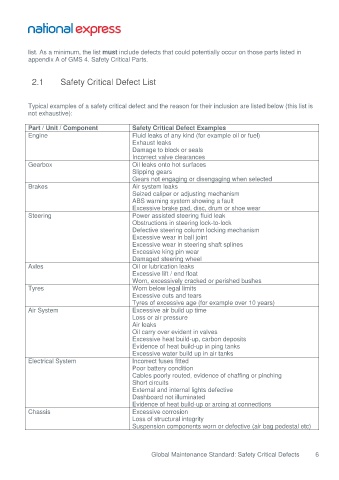
2.1 Safety Critical Defect List
Typical examples of a safety critical defect and the reason for their inclusion are listed below (this list is
not exhaustive):
Part / Unit / Component Safety Critical Defect Examples
Engine Fluid leaks of any kind (for example oil or fuel)
Exhaust leaks
Damage to block or seals
Incorrect valve clearances
Gearbox Oil leaks onto hot surfaces
Slipping gears
Gears not engaging or disengaging when selected
Brakes Air system leaks
Seized caliper or adjusting mechanism
ABS warning system showing a fault
Excessive brake pad, disc, drum or shoe wear
Steering Power assisted steering fluid leak
Obstructions in steering lock-to-lock
Defective steering column locking mechanism
Excessive wear in ball joint
Excessive wear in steering shaft splines
Excessive king pin wear
Damaged steering wheel
Axles Oil or lubrication leaks
Excessive lift / end float
Worn, excessively cracked or perished bushes
Tyres Worn below legal limits
Excessive cuts and tears
Tyres of excessive age (for example over 10 years)
Air System Excessive air build up time
Loss or air pressure
Air leaks
Oil carry over evident in valves
Excessive heat build-up, carbon deposits
Evidence of heat build-up in ping tanks
Excessive water build up in air tanks
Electrical System Incorrect fuses fitted
Poor battery condition
Cables poorly routed, evidence of chaffing or pinching
Short circuits
External and internal lights defective
Dashboard not illuminated
Evidence of heat build-up or arcing at connections
Chassis Excessive corrosion
Loss of structural integrity
Suspension components worn or defective (air bag pedestal etc)
Global Maintenance Standard: Safety Critical Defects 6