Page 203 - PARPAR-2
P. 203
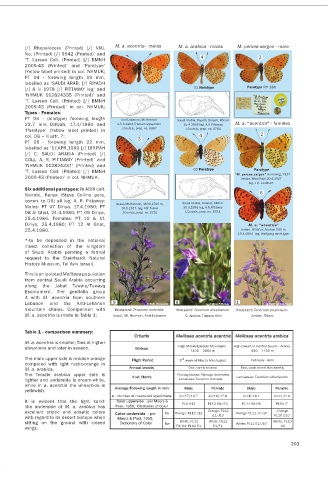
Melitaea acentria Lukhtanov (2017) Hermon Fritillary [/] Rhopalocera (Printed) [/] VIAL M. a. acentria - males M. a. arabica - males M. persea sargon - male
No. (Printed) [/] 9542 (Printed)’ and
‘T. Larsen Coll. (Printed) [/] BMNH 4 3
Endemic to the Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon mountain %LRORJ\ 2009-43 (Printed)’ and ‘Paratype’
ranges in Israel (its TL), Lebanon and Syria. Wolfgang (Yellow label printed) in col. NHMUK;
ten-Hagen found relict population in the eastern slopes PT 04 - forewing length 19 mm,
of Jabal al-Druze, S Syria above 1400 m – illustr. 1, this )OLJKW SHULRG second week of May at 1400 m to mid-
# labelled as ‘SAUDI ARAB. [/] RIYADH
isolated population is the dwindling bridge from the TL August at 2800 m Mt Hermon S Anti-Lebanon ridge, [/] 8 iii 1978 [/] PITTAWAY leg’ and 01 Holotype Paratype RH 386
to the Jordanian remnants of ex “M. didyma sargon” Israel (Benyamini, 1990a: 128 as Melitaea persea ‘NHMUK 012824335 (Printed)’ and
(Hemming, (1932) – illustr, 2 & a rare female (leg. ten- montium); June 1900 Anti-Lebanon as M. didyma var. ‘T. Larsen Coll. (Printed) [/] BMNH
Hagen) - illustr. 3) and further ~1300 km SE to the endemic persea (Nicholl, 1901); 27 June 1931 at “Djebel Makmal 2009-43 (Printed)’ in col. NHMUK;
C Saudi Arabian Melitaea acentria arabica Benyamini, in 2600-2800 m” (~ 10 km NE Bscherré) N Lebanon as M. 7\SHV - )HPDOHV
21603-BRACHA-PARPAR - 21603-BRACHA-PARPAR | 13 - B | 21-12-30 | 11:34:48 | SR:-- | Magenta
21603-BRACHA-PARPAR - 21603-BRACHA-PARPAR | 13 - B | 21-12-30 | 11:34:48 | SR:-- | Yellow
#21603-BRACHA-PARPAR - 21603-BRACHA-PARPAR | 13 - B | 21-12-30 | 11:34:48 | SR:-- | Black
21603-BRACHA-PARPAR - 21603-BRACHA-PARPAR | 13 - B | 21-12-30 | 11:34:48 | SR:-- | Cyan
Pittaway and Coutsis 2021 n. ssp – see next entry. Since didyma ab. wullschlegeli Oberthür, 1909 (Zerny, 1932); PT 05 - (allotype) forewing length
Anti-Lebanon, Mt.Hermon
2008 protected by law in Israel. The first three specimens May 1927-34 at Bwarij (Bouarej, 1400+ m, Mt Lebanon 23.7 mm Diriyah, 17.4/1980 and 2-5.6.1864,Tristram expedition Saudi Arabia, Riyadh, Diriyah, 450 m M. a. ´acentriaµ - females
25.4.1980 leg. A.R.Pittaway
RI WKLV VSHFLHV WZR ʇʇ DQG RQH ʆ QRZ LQ WKH +RSH range, C Lebanon) as M. saxatilis ssp. montium (Ellison & ‘Paratype’ (Yellow label printed) in J.Coutsis, prep. no. 5867 J.Coutsis, prep. no. 5754
Museum, Oxford University), were collected between 2-5 Wiltshire, 1939); May-June (first brood) and July-August col. DB – illustr, 7; 4 2
June 1864, during the 1863-1864 expedition of Henry (second brood), above 1500 m to “high levels in the PT 06 - forewing length 22 mm, 5
Baker Tristram, when his party rode up Mt Hermon from Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon ranges”, Lebanon (Larsen, labelled as ‘17.APR.1980 [/] DIRIYAH
‘Rasheiya’ (Rachaiya el Foukhar), Syrian Anti-Lebanon 1974: 125-126 as Melitaea persea montium); 29 June [/] C. SAUDI ARABIA (Printed) [/]
(Tristram, 1865: 602-610; Benyamini, 2019d, Benyamini 1996, 1900-2000 m 15-20 km W Qarah N Syrian Anti- COLL. A. R. PITTAWAY (Printed)’ and
& Hogan, 2020 – illustr 4.). It was described by Lukhtanov Lebanon (ten-Hagen, 1998 – as M. (didyma) persea ‘NHMUK 012824337’ (Printed) and
(2017) from 37 holotype & paratypes* collected from montium & pers. comm. to DB - illustr. 6); 1 May 1995 in ‘T. Larsen Coll. (Printed) [/] BMNH 02 Paratype Paratype
early May to early July between 1750 and 2050 m on “Reschide” (Rushaydah) 800-1400 m and Busan 1500 2009-43 (Printed)’ in col. NHMUK. ´M. persea sargon” Hemming, 1932
the SW slopes of Mt Hermon, S Anti-Lebanon mountain m both at the eastern slopes of Jabal al-Druse of Syrian Jordan, Wadi Rajil 20.4.1927
leg. l. K. Lockhart
range. Differences in genitalia and DNA clearly separated Hauran (det. John Coutsis Athens Greece and ten-Hagen 6L[ DGGLWLRQDO SDUDW\SHV Ln ABRI coll.
it from Turkish-Iranian M. persea, defining acentria pers. comm. to DB); 1828-2602 m in Al-Lazzab reserve Nairobi, Kenya (Steve Collins pers. 6
as a new species. Based on DNA analysis, Lukhtanov Syrian Anti-Lebanon, Syria (Zarikian & Ghrejyan, 2018); comm. to DB) all leg. A. R. Pittaway:
concluded that M. acentria is the result of speciation, 19 April 1993 between Na’ur (Amman) and the Dead Males: PT 07 Diriya, 17.4.1980; PT Israel, Mt.Hermon, 1600-1700 m, Saudi Arabia, Al Ghat, 680 m
1-1.6 MYA, of hybrids of M. persea that became isolated 6HD P -RUGDQ ʆ OHJ WHQ +DJHQ SHUV FRPP 08 Al Ghat, 24.4.1980; PT 09 Diriya, OHJ 2ÀU 7RPHU 30.3.1983 leg. A.R.Pittaway
J.Coutsis, prep. no. 5753
J.Coutsis, prep. no. 5751
from the main northern stock in the Levant ‘refugia’ to DB – illustr. 3); 20 April 1927 Wadi Rajil, NW Jebel 25.4.1980. Females: PT 10 & 11
(hybrid speciation). He also figured ‘M. didyma liliputana’ Kurma (“20 miles E. of Qasr Azraq”), N Jordan on the Diriya, 25.4.1980; PT 12 Al Ghat,
M. a. ´acentriaµ
(presented in this book as M. israela n. sp.) that flies south-eastern periphery of Jabal al-Druze, Hauran, Syria 25.4.1980. Jordan, W Na’ur, Amman 500 m.
together with M. acentria. Lukhtanov showed them to +HPPLQJ DV D ʆ SDUDW\SH RI M. didyma sargon 19.4.1993 leg. Wolfgang ten-Hagen
be genetically separate, but failed to compare it with M. ssp. nov. – illustr. B&W in Pls. XV & XVI and illustr 2). *-to be deposited in the national
didyma libanotica (Belter, 1934) that flies lower down at insect collection of the kingdom
the bottom of the Rift Valley and the east-facing slopes of /LIH KLVWRU\ univoltine with a questionable partial of Saudi Arabia pending a formal
Ramim - Naftali Ridge, N Galilee and S Lebanon, breeding second brood, wherever the dominant LHP (Plantago request to the Steinhardt Natural
on a completely different LHP (see entry for this species). lanceolata - illustr. 7) is green and available to larvae. History Museum, Tel Aviv Israel).
However, acentria and israela sometimes hybridize Two fertile females that were collected on 5 June 2018,
(illustr. 5), suggesting that M. didyma was possibly the at the TL between 1750 and 1850 m, laid batches of This is an isolated Melitaea population
other ancestral origin of acentria. Resembles M. didyma eggs under lower leaves of P. lanceolata . The first from central Saudi Arabia occurring
and M. trivia, differing from M. didyma mainly by the arc female laid batches of 17 and 19 eggs, 10 mm apart along the Jabal Tuwaiq/Tuwayq
of orange spots on the unh, which are reduced, more under the same leaf; the second female also laid two Escarpment. The genitalia group
separated and sometimes individually encircled in black. batches, of 7 and 48 eggs, 10 mm apart, under a nearby it with M. acentria from southern
Also differs by its biotope preferences, with M. acentria leaf. The light green glossy eggs are 0.6 mm in diam., Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon 9 'XEL %HQ\DPLQL 8 7RQ\ 3LWWDZD\ 1 2UL )UDJPDQ 6DSLU
usually found at higher altitude, never below 1400-1500 slightly elongated upwards, with 26-28 indistinct ribs mountain chains. Comparison with Hostplant: Teucrium orientale Hostplant: Teucrium oliverianum Hostplant: Teucrium pruinosum
m (Larsen, 1974; DB, pers. obs.). Differs from M. syriaca at the upper section of its height (four eggs examined). M. a. acentria is made in Table 1: Israel, Mt Hermon, Anti-Lebanon C. Arabia, Tuwayq Hills Jordan, Edom
(ex M. trivia) by the lack of black spots forming an arc The top of the egg is flat with small protrusions. Before
between the discal and postdiscal areas on the uph. hatching, the egg turns grey with a black top. L1 hatched
Males are typically reddish (Pl 4 A12, close to Terracotta, in the lab. after five days, eating the upper part of the 7DEOH FRPSDULVRQ VXPPDU\ Criteria 0HOLWDHD DFHQWULD DFHQWULD 0HOLWDHD DFHQWULD DUDELFD
per Maerz & Paul, 1950), individuals sometimes varying eggshell or sometimes all. L1 is 1.5 mm long, yellowish,
in the intensity of black spotting. Females are usually with seven longitudinal rows of long black hairs emerging M. a. acentria LV VPDOOHU ÁLHV DW KLJKHU High Middle Eastern Mountains High Desert in Central Saudi – Arabia
elevations and later in season.
larger and lighter: between Amber-glow to Burma (Pl 12 from tiny grey protrusions over the larval skin. As it starts Biotope 1400 – 2800 m 450 – 1150 m
I10) and Spruce (Pl 12 K8), sometimes having a greyish nibbling at the LHP epidermis, producing indentations, The male upper side is reddish-orange nd
ground colour. These southern Levantine populations its colour turns to greenish-light grey. The heart-shaped compared with light rustic-orange in Flight Period 2 week of May to Mid August February - April
are isolated from M. persea of SE Turkey by ca. 500 km head is a glossy dark brown with white and black hairs. M. a. arabica. Annual broods One, rarely second Two, each brood flies shortly
(Hesselbarth et al., 1995(3): 827). L1 are gregarious, sometimes developing beneath a The female arabica upper side is Host Plants Plantaginaceae: 3ODQWDJR DWUDWD Lamiaceae: 7HXFULXP ROLYHULDQXP
Plantaginaceae: 3ODQWDJR DWUDWD
lanceolata
Lamiaceae: 7HXFULXP RULHQWDOH
loose protective web. At L2, develops from 2.7 to 5.5 mm lighter and underside is cream-white, Lamiaceae: 7HXFULXP RULHQWDOH
in length and at L3 to 7.5 mm. L3 is beautifully decorated while in a. acentria the underside is Average Forewing length in mm Male Female Male Female
with eight longitudinal rows of cones in the first four yellowish.
*- All types of this protected species were first deposited in the Zoological segments, followed by 13 further rows. Cones vary in n - number of measured specimens ( n=17 ) 16.7 ( n=16 ) 17.8 ( n=4 ) 18.1 ( n=2 ) 22.8
Institute of the Russian Academy of Science (St. Petersburg) (Lukhtanov size, and are white, yellow or orange, usually with black It is evident that the light sand- Color upperside - per Maerz & PL4 H12 PL12 K8/i10 PL11 H8-H9 PL10 i7
et al., 2017), but were requested to be returned to the Steinhardt Natural like underside of M. a. arabica has Paul, 1950, Dictionary of Color
History Museum, Ramat Aviv, Tel Aviv, Israel, where fourteen paratypes spines. The prolegs are white with black crochets. The excellent criptic and adaptic colors Color underside - per fw Orange: PL12 J12 Orange: PL12 Orange: PL11 J7-J10 : Orange
are presently deposited (Ariel-Leib Friedman, Tel-Aviv University, pers. head is orange with black mandibles, eyes and hairs. with regard to its desert biotope when Maerz & Paul, 1950, i11/J10 PL10 D10
comm. to DB). Most L3 spread over the LHP base, singly or up to three sitting on the ground with closed Dictionary of Color hw White: PL11 White: PL12 White: PL11 E2/J10 White: PL10
larvae together, prior to overwintering. Others hibernate wings. F2/G4; PL12 E1 E1/F1 C2
198 203